Building RESTful APIs with Laravel: Everything You Need to Know
Listen to this article

When developing modern web applications, the framework you choose directly impacts the performance, scalability, and long-term maintainability of your RESTful APIs. Among PHP frameworks, Laravel stands out for its well-defined structure, extensive ecosystem, and overall ease of use.
A 2024 academic study evaluating RESTful API performance found that Laravel delivered response times 1,745.7 milliseconds faster on average than Express.js (Node.js), highlighting its ability to handle real-world workloads efficiently.
Laravel comes with integrated routing, middleware, request validation, authentication, and testing capabilities to help developers build secure, scalable, and maintainable RESTful APIs without relying heavily on external libraries. Its modular architecture and expressive syntax make it easier to adapt and scale applications as business needs evolve.
This article explores best practices for building RESTful APIs in Laravel, focusing on clean architecture, performance optimization, security, and long-term maintainability.
In a Nutshell
Laravel is ideal for building safe and scalable RESTful APIs. It has features like authentication, validation, version control, and tools to make the process run smoothly. It's a solid choice for real-world apps in e-commerce, fintech, and enterprise applications.
Understanding RESTful APIs
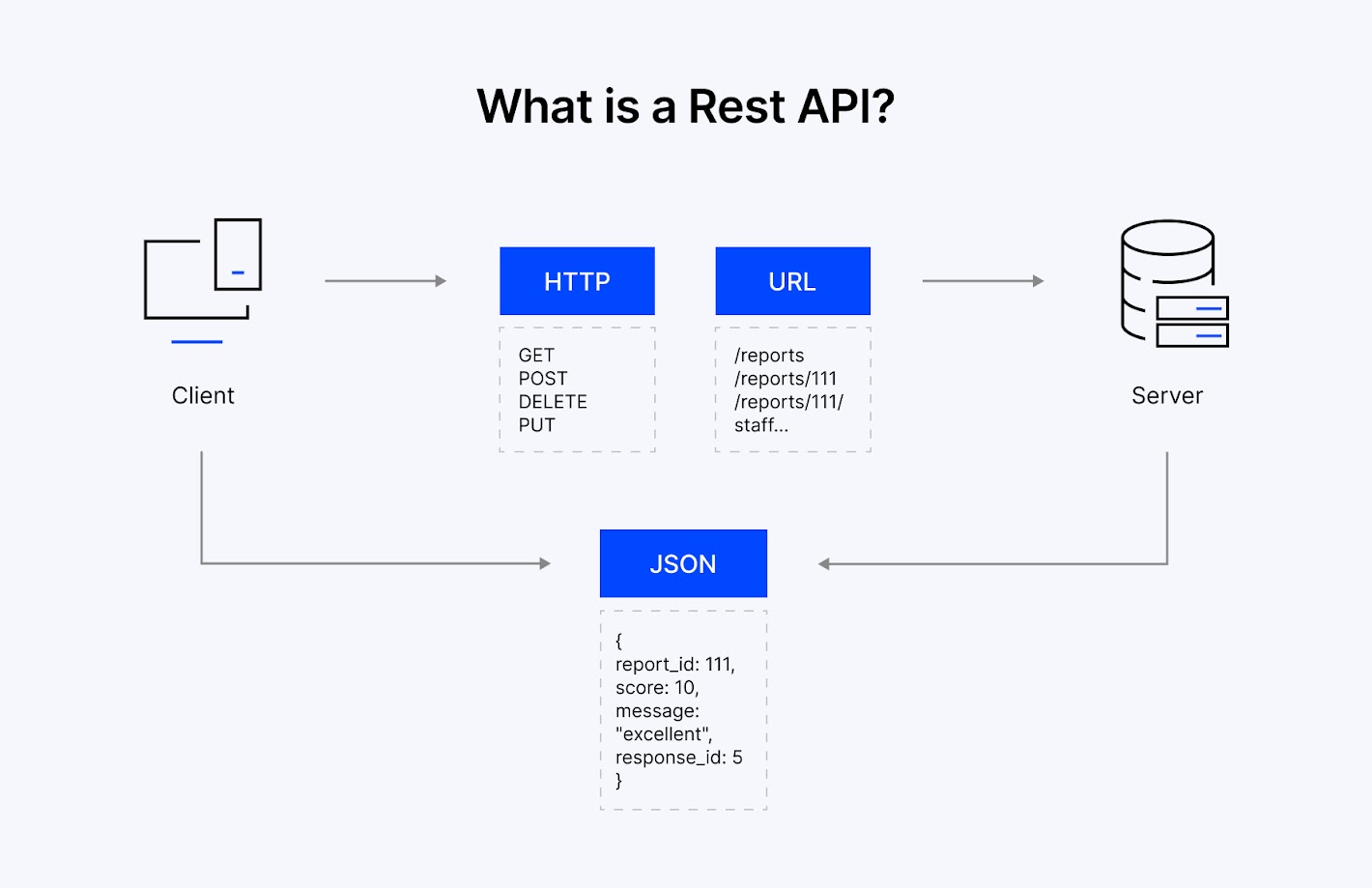 RESTful APIs are a way for web services to communicate with each other using common HTTP methods. They enable flexible service setups, unlike older applications, where all features were in one codebase. REST APIs enable the modular, service-oriented architectures necessary for today's businesses to integrate and be agile.
RESTful APIs are a way for web services to communicate with each other using common HTTP methods. They enable flexible service setups, unlike older applications, where all features were in one codebase. REST APIs enable the modular, service-oriented architectures necessary for today's businesses to integrate and be agile.
REST principles include statelessness, a consistent interface, and resources. Each of these principles provides real-world benefits, such as reducing complexity, improving system maintainability, and enabling integration with third-party services.
When building a RESTful API with Laravel, remember these principles. They'll help you create systems that work well with different clients, websites, mobile apps, and other integrated services, all using a single backend. This allows you to reduce development overhead while ensuring consistent data handling.
The advantages of REST APIs being stateless support scalability in applications. All the necessary information is contained in each request. There are no server-side session dependencies that could create issues for clients with high input during heavy traffic. This enables horizontal scalability strategies, which are beneficial for businesses planning to grow in the future.
Why Laravel Is Strategic For API Architecture
‣ Laravel’s Ecosystem and Community Maturity
Laravel's strong community keeps the framework up-to-date with industry standards. Because the community develops and maintains it, it's constantly improving. Laravel has over 80,000 stars on GitHub and thousands of contributors around the world. It keeps up with technology while making sure not to break up older systems.
‣ Built-in Capabilities for Rapid, Secure, and Scalable Laravel RESTful API development
Laravel's built-in features speed up secure API development. Eloquent ORM, which has tools inside it, helps stop SQL injection attacks by using queries with parameters. Also, the middleware system lets you put security rules in one place and make sure they are followed.
Laravel's validation makes sanitizing user input easy, often doing a more thorough job than if you built it yourself. This helps cut down on security problems.
‣ Compatibility with Existing Enterprise Stacks and Cloud Platforms
Enterprise compatibility is another strategic advantage. Laravel integrates easily into existing technology stacks and is compatible with various database systems, caching options, and cloud service providers. Laravel can even utilize native integration features for organizations using AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. This reduces infrastructure complexity and deployment effort.
Building for Scale: Architectural Considerations
• Modular Monoliths vs. Microservices in Laravel
Modular monoliths in Laravel give businesses a flexible option. Structuring code into modules with clear boundaries can help teams achieve many of the same benefits of microservices. But without the complications of working within distributed systems. This is a suitable approach for organizations with smaller development teams or for organizations that are just beginning their journey into APIs.
Laravel’s service container and provider system easily support a modular approach. Isolating business logic in service classes lets controllers focus on HTTP tasks. This setup simplifies testing and maintenance. If your business needs change, it can even make moving to microservices easier.
Microservices architecture can be beneficial when teams can manage the additional operational complexity. Laravel is lightly structured but well-suited for each individual microservice. Both Laravel Horizon and Laravel Telescope can help monitor activity across different services.
• API Versioning and Future-Proofing Systems
It's important to get your API versioning sorted out early. This helps prevent client application issues when you push out updates that might break the application. The Laravel routing system can manage API versioning by including separate namespaces and utilizing middleware. Another good idea is to use semantic versioning. This lets API users know how big the changes are, and it helps you support smoother migration processes.
Database design considerations can greatly impact scalability. Laravel has a migration system for managing database schema changes with version control. When using Eloquent relationships, keep query performance in mind, mainly as your data grows. As the data set grows, proper indexing and query optimization become essential.
Setting up a Laravel Project for API Development
1. Creating a New Laravel Project
You can start Laravel RESTful API development with Composer installation and environment setup. Create a new project, for example, with composer composer create-project laravel/laravel mytest, and then configure the environment file (.env) with details for the connection to the database, caching, and connections to other services.
2. Configuring the Database
Database setup involves more than just connection parameters and includes performance optimization options. By configuring database pooling, query logging, and migration settings, you can ensure that you get the best performance from the development stage through production.
Update the .env file with your database credentials.
3. Creating a Model and Migration
Creating models and migrations follows Laravel conventions as well as your business logic requirements. You will create model classes and migrations with php artisan make:model Product -m. All migrations should include indexing on columns that are queried frequently, as well as foreign key relationships to ensure data integrity.
Add in the generated migration:
4. Building the API Routes
To set up API routes in Laravel, use the dedicated API route files and middleware groups. This helps follow RESTful practices by using the correct HTTP methods and resource names. Also, route model binding makes controller code simpler and automatically finds the correct models.
In routes/api.php:
5. Creating the Controller
Run php artisan make:controller ProductController --api to create a controller with methods for standard REST actions.
Standard controller method:
Controllers are responsible for handling HTTP requests and responses only, not business logic.To keep your controller clean, move business logic to service classes or model methods. This way, you can easily test them by creating mocks.
6. Implementing CRUD Operations
In CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations, you need to keep checking inconsistencies in error handling, response formatting, and input validation. Laravel's resource classes help ensure your JSON responses are consistent, while form requests are used to isolate the validation logic from controller methods.
Use Form Requests for validation and Resource Classes for JSON responses:php artisan make:request StoreProductRequestphp artisan make:resource ProductResource
7. Testing the API
Separate tests into those that test the business logic and feature tests that cover the entire request-response flow. During testing, the Laravel testing tools let you add data to your database, send HTTP requests, and verify the format and status of responses.
Write feature tests and unit tests separately.
Example feature test:
RESTful API Design Best Practices
1. Align API Design with Business Goals
The design of an API should never be separate from business processes and domain models; rather, the API should be an extension of them. Consequently, APIs must feel natural for use, and they should be governed by business rules. Resource names should use terms that are considered familiar among stakeholders as well as among consumers of the APIs.
2. Adopt a Versioning Strategy Early
From the very start, add versioning when you launch your API. This way, future updates won’t break anything for people who are already using it. In Laravel, you can manage versions with route prefixes, controller namespaces, and middleware. Using semantic versioning also lets your users know exactly what kind of changes to expect.
3. Ensure Consistent and Predictable Responses
Consistency among all API endpoints is what we see in Laravel, which simplifies integration for client developers. Laravel's API resource classes have standard response formats and consistent ways to show errors. This helps client apps deal with issues more smoothly.
4. Implement Scalable Authentication & Authorization
How you choose an authentication strategy has security and scalability implications. Sanctum provides token-based authentication for SPA (Single Page Applications) without requiring complex authorization logic.
Taylor Otwell, who created Laravel, said how important this setup is for actual projects:
I spent some time today making our Next.js frontend example and Laravel Sanctum API backend better. I updated to Next.js 12 and worked on making the documentation easier to understand.
— Taylor Otwell, Creator of Laravel
On the other hand, Passport is designed to implement OAuth2, so it’s mainly used where more complex authorization workflows are needed beyond simple token-based access. Policy classes handle authorization in a detailed, specific way, keeping that logic separate from your controllers.
5. Prioritize Data Validation and Input Sanitization
Validating inputs helps to avoid security vulnerabilities and data corruption. Laravel form request classes help you keep your validation rules organized and tidy up error responses. Custom validation rules in your application for business validation require more than just type checks.
6. Leverage Logging and Monitoring for Observability
Good logging is for tracing issues early and monitoring performance. Laravel logging provides multiple channels and allows sending logs to external services. By using structured logging with context, redundancy is minimized, patterns are easily spotted, and problems are quickly resolved.
7. Optimize for Performance and Efficiency
To get the most out of your RESTful API, keep performance and efficiency in mind. Some ways to do this include making database queries better, using caching, and keeping response sizes small. The system interacts well with databases, using tools like Laravel's Query Builder. Think about using caching systems such as Redis. It can reduce the number of times you access the database.
8. Ensure Developer-Focused Documentation
The API documentation is the first idea of how APIs communicate with users and also serves as a guide for new programmers. Endpoints have, fortunately, some amount of excellent documentation using tools like Scribe (Laravel's documentation generator) or Postman collections. Providing code samples and request/response examples helps developers to integrate more quickly.
9. Plan for Integration Flexibility
When planning future designs, it's important to consider how they will integrate with other systems. Version control, multiple response formats, webhooks, and adaptable data models really enable smooth integrations with third parties. Laravel's event system is good for notifying outside systems. The main code and the outside system stay separate, as long as the subprocess is done.
Want experts to design your RESTful API architecture?
Let's talkLoading...
Real-World API Use Cases
‣ E-commerce Platform Integration
Laravel API implementations are widely used for modern e-commerce platforms because Laravel acts as an intermediary to connect various back-office systems that manage inventory, payment processing, and customer service. A common example of an e-commerce API built in Laravel includes keeping product catalogs synchronized between sales channels, updating real-time inventory levels, and managing customer orders.
During peak shopping times, these systems can manage thousands of requests per minute. Queues allow Laravel to defer the processing of time-consuming tasks (such as order fulfillment, email notifications, or inventory syncing). So, dealing with one customer's request won't slow down other customers browsing the website. It also supports fast delivery of product components because the framework caches data, whether for web or mobile, so loads happen quickly.
‣ Fintech Application Backend
Laravel RESTful API is a powerful means for applications in financial technology to control their sensitive data while avoiding regulatory issues. Secure transaction flows, account management, and financial reporting are the three most prominent features of Laravel, which is why it is considered one of the most secure PHP frameworks.
Most of these applications interact with the outside world, such as payment processors, credit agencies, and regulatory systems. Laravel's HTTP client makes it simple to work with external APIs. Moreover, its logging features provide an audit trail that fits what financial regulations require. Fintech teams often hire API developers to handle these sensitive integrations securely and efficiently.
‣ Internal Business Tool Connectivity
Large firms utilize RESTful APIs in Laravel solutions to connect different internal systems such as CRM software, accounting tools, and project management applications.
For instance, Slashdev.io developed a mobile application using Laravel as the backend, providing a RESTful API to handle requests from the React Native frontend. This helped with efficient communication between the server and client, enhancing the performance and scalability of the application.
RESTful APIs in Laravel allow data synchronization between departments without compromising the independence of individual systems and help decrease manual entries.
With Laravel, systems can now grow on their own while keeping data consistent using well-defined API agreements. The built-in testing makes sure changes in one system won't break how it works with others.
Bottom Line
Building a durable Laravel API that serves both business and technical teams requires careful planning. From how you structure everything to keeping them secure and fast, these will help you create systems that grow with your business needs while staying efficient.
For APIs to work well, you need to focus on security, speed, and how easy they are to maintain. Introducing strong authentication systems, wide monitoring, and a healthy practice in codebases will allow the organization to mature and remain at low operational costs for years to come.
Make sure your Laravel API strategy supports your overall digital plans. So, any technical investments solve actual business needs and don't cause technical or structural problems. This is essential as companies are moving towards cloud-native architectures, CI/CD practices, and incorporating new technologies.
So the future of Laravel development will include AI, serverless computing, and edge computing in more and more upcoming projects with the latest changes. Laravel's adaptable design, along with its community-driven development, helps it to meet the demands of upcoming applications while still supporting current projects.
Being a leading Laravel development company, Webandcrafts offers comprehensive Laravel development services, including custom REST API development services tailored to specific business workflows and system integrations. With experience from many enterprise Laravel projects, like building the backend for the Caribou Coffee Kuwait mobile app, our team ensures your API setup supports your current needs and future growth.
Ready to launch secure and reliable Laravel APIs?
Let's talkLoading...
Discover Digital Transformation
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.










