Top 10 Advantages and Disadvantages of Node.js

Node.js has established itself as a popular backend choice for companies that want to develop fast, scalable, and efficient web applications. According to both Statista and the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, Node.js was the leading backend technology in 2024, used by 40.8% of developers worldwide. It was especially favored by those learning to code (44.2%) and remained widely adopted among professional developers (40.7%) and other coding professionals (38.1%).
Node.js has helped companies like Walmart and IBM to enhance performance, optimize response times to client requests, and minimize complexities in their development practices.
Node.js has several advantages with its non-blocking, event-driven architecture that allows it to handle thousands of simultaneous connections and is a great fit for real-time applications.
While this all seems great, there are limitations to consider about Node.js. For instance, Node.js runs on a single thread by default, so handling heavy multithreaded tasks often requires extra setup with worker threads. For that reason, it’s not always the best fit for applications that need true parallel processing, like data-intensive computations.
The purpose of this blog is to give a detailed overview of Node.js's advantages and disadvantages so that you can evaluate Node.js based on its specific use cases. By reading this blog, you'll have a clear idea of when to use Node.js and when not to. Keep reading to understand more.
In a Nutshell
Node.js is an efficient, developer-friendly backend technology that is ideal for building real-time applications like chat apps, APIs, and streaming platforms. Node.js allows developers to use JavaScript on the back end and has the capability to support modern development approaches. However, it is not the right option for CPU-bound tasks such as video processing or complex financial systems, as it is single-threaded.
What Is Node.js?
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform runtime JavaScript environment launched in 2009 by Ryan Dahl. Node allows developers to run JavaScript outside of the browser on servers and the operating systems themselves. This was a big transformational change, helping expand JavaScript from a primarily client-side language into a widely adopted tool for backend development.
Node.js operates on the Google Chrome V8 engine, which is built with C++. The V8 engine uses a technique called Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation that takes JavaScript code and converts it to machine code that your computer can understand. It optimizes frequently used code, speeding up the time it takes to execute code. JIT optimization is well-suited for high-performance applications.
Node.js stands out due to two core architectural features.
Non-Blocking I/O: It handles multiple operations simultaneously without waiting for each operation to finish. In other words, applications can reply to a request more quickly while consuming slightly fewer resources.
Event-Driven Architecture: Node.js manages asynchronous operations efficiently with the help of an event loop. Therefore, Node.js can handle thousands of simultaneous connections without much memory usage.
These features make it easier for developers to create real-time apps like chat tools, APIs, and streaming platforms.
Google Trends search interest graph also indicates that Node.js is getting popular among users worldwide over time.
Node.js Server Architecture
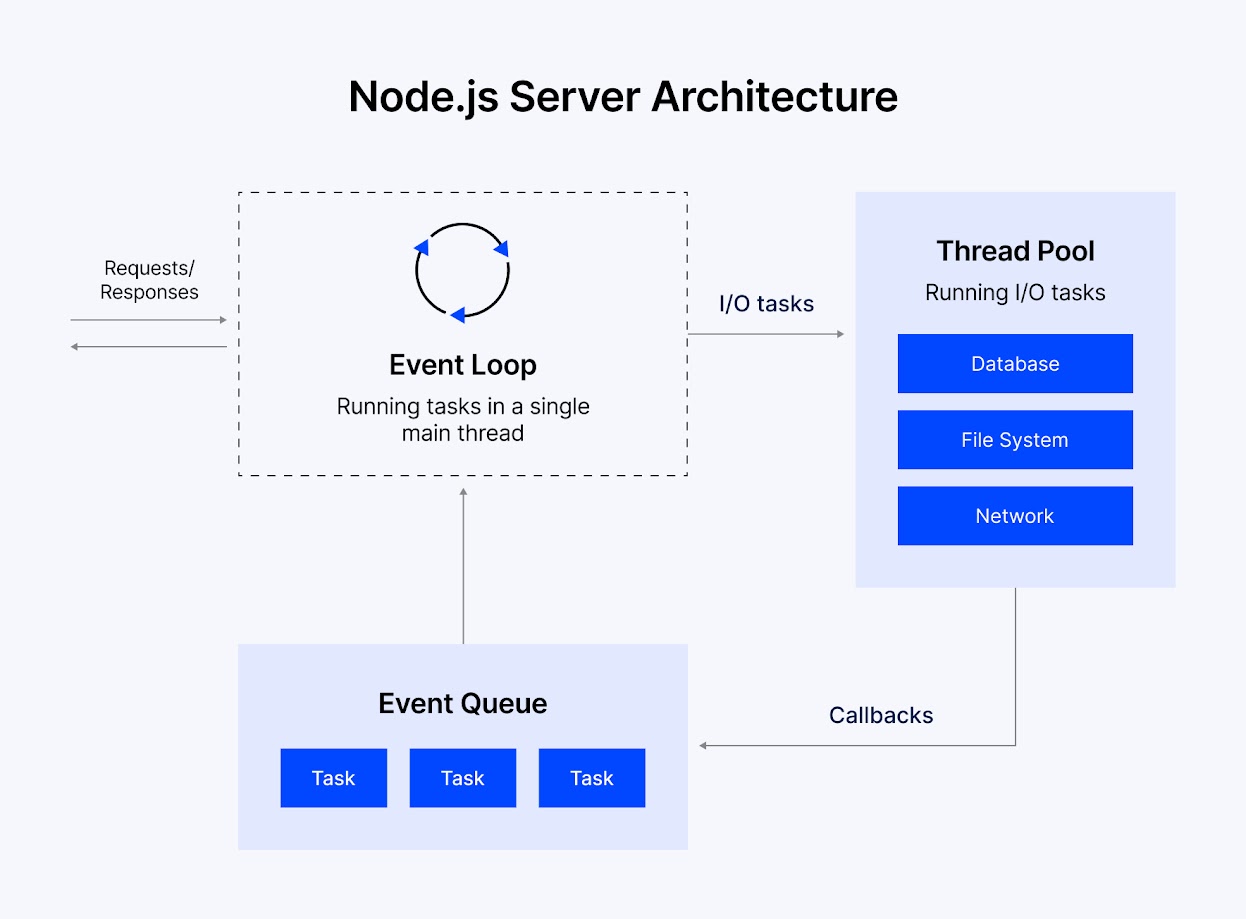 Node.js architecture consists of a single-threaded event loop and a worker thread pool. The event loop handles asynchronous operations and runs on the main thread by handling JavaScript processes, input output callbacks, and timers through sequential phases. The thread pool manages blocking operations.
Node.js architecture consists of a single-threaded event loop and a worker thread pool. The event loop handles asynchronous operations and runs on the main thread by handling JavaScript processes, input output callbacks, and timers through sequential phases. The thread pool manages blocking operations.
Node.js uses a C++ library known as libuv that makes Node.js asynchronous. By executing tasks in the background, libuv helps with file reading, networking, and threading. Libuv is the library that organizes how tasks are processed, where fast async tasks go through an event loop while slow or blocking tasks go to the thread pool.
The role of the thread pool is to handle file input and output actions. Usually, a thread pool has four threads, but the number of threads can be configured with an environment variable called UV_THREADPOOL_SIZE. The purpose of this environment variable is to ensure that time-consuming operations do not block the event loop and keep the application responsive. Using a few resources, the event loop, libuv, and thread pool function together to maintain high throughput.
Advantages of Node.js
1. High Performance and Scalability
The V8 engine used by Node.js compiles JavaScript code into optimized machine code using JIT compilation. This allows JavaScript programs to be run very quickly, enabling enterprise-level applications such as Netflix and PayPal to offer a more cost-efficient service by improving performance and reducing latency. PayPal’s Node.js app doubled the number of requests per second and reduced response times by 35% compared to their previous Java version.
Similarly, Ryder, a leading logistics company, adopted Node.js to replace their outdated infrastructure, improving system performance and enabling faster development cycles.
2. Non-Blocking, Event-Driven Architecture
As mentioned above, Node.js handles simultaneous connections with very little memory overhead, compared to traditional blocking I/O models used in many multi-threaded servers.
3. Single Programming Language (JavaScript)
By using JavaScript consistently across frontend and backend, teams can limit context switching, streamline workflows, and reuse code, making full-stack development easier.
Node.js lets us use JavaScript on both the client and server sides, so our developers can work across the whole system. This makes it easier to collaborate and quickly address user needs at any point in the stack.
4. Large Ecosystem with NPM (Node Package Manager)
NPM contains over 2 million live packages and serves tens of billions of downloads. The large repository facilitates and speeds up development by providing built-in solutions and components.
5. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Node.js is available natively on Windows, macOS, and Linux, enabling teams to use one codebase across all platforms and reducing deployment and infrastructure challenges.
Major cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure support Node.js on both Linux and Windows environments, which makes cross-platform deployment even easier.
6. Real-Time Capabilities
Node.js is great for real-time applications like chat, gaming, live collaboration, and streaming, with its built-in WebSocket support. For example, Slack even provides an official Node.js API that uses WebSockets to keep messages and updates in sync instantly.
7. Vibrant Developer Community and Support
Node.js is supported by the constant contributions of individual developers and large technology companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft (members of the OpenJS Foundation), which ensures regular updates and long-term reliability. It has more than 110,000 stars and 3,580+ contributors on GitHub, which is an indication of the community support for Node.js.
8. Faster Development with Node.js Frameworks
Node.js Frameworks like Express.js, Koa.js, and NestJS provide routing, middleware, and security by default. For instance, official benchmarks from Fastify show that Koa can handle approximately 37,639 requests/second while maintaining the lowest average latency, good for handling concurrent requests.
9. Efficient Handling of I/O Bound Tasks
Node.js performs well in I/O-heavy environments (file systems, databases, APIs) and uses its event loop with non-blocking I/O to minimize execution delays, making it a suitable environment to build microservices, APIs, and stream-based apps.
10. Perfect for Microservices Architecture
Its lightweight run-time, modular approach is best suited for microservices, where teams can develop, test, scale, and deploy independent services. Many companies, such as Uber and PayPal, have utilized Node.js for microservices because of its efficiency and small resource footprint.
Disadvantages of Node.js
1. Callback Hell and Asynchronous Code Management
Nested callbacks are often known as "callback hell", and they can lead to deeply indented, hard-to-read, and error-prone code, particularly in the case of older code or new code written by new developers. Both Promises and async/await help reduce this, but many developers still find it challenging to manage asynchronous logic effectively.
Callback hell was a serious trouble in the past, but async/await/promises help now to overcome it. However, you’ll still face this issue in outdated code from Junior developers.
— Alex Aslam, JavaScript developer and writer.
2. Not Suitable for CPU-intensive Applications
Node.js is a single-threaded runtime and isn’t ideal for workloads involving heavy computation since heavy computation blocks the event loop, reducing responsiveness. For example, image processing, scientific computing, etc. These kinds of workloads block the event loop, thereby degrading responsiveness. To handle such heavy tasks across multiple CPU cores, you need to use built-in modules like cluster or worker_threads, which might make your app’s design more complex.
A study on arXiv shows how CPU-bound tasks block the event loop and affect performance in Node.js apps.
3. Lack of a Strong Standard Library Compared to Other Languages
Compared to Java or Python, Node.js has a more minimal built-in standard library, so developers often rely on external NPM modules for common tasks like validation, encryption, or file manipulation. This can increase dependency risks and long-term maintenance overhead.
A paper on arXiv highlights how Node.js relies on third-party modules even for common tasks.
4. Smaller Pool of Skilled Developers
Even though JavaScript is widely used, finding highly skilled Node.js developers proficient in non-blocking I/O, asynchronous patterns, event-loop management, and production-grade architecture can be challenging, making experienced talent relatively more expensive.
For instance, a report by Agency partners says that demand for Node.js developers in the UK is much higher than the available talent, which makes hiring more difficult. In order to overcome this resource shortage, many companies are turning towards trusted development partners who can provide skilled and experienced Node.js developers.
5. Difficulty in Handling Multi-Threading
worker_threads helps in parallel computation, but each worker thread has its own V8 instance, and thus causes significant overhead. Worker threads are not ideal for I/O tasks, can make debugging harder, and create more complicated issues with memory sharing. The best way to exploit worker threads is with thread pools and careful design.
A study found that while Node.js can run tasks in parallel using worker threads or child processes, both methods have performance limits and complexity.
6. Limited Support for Heavy Computation Tasks
CPU-bound work, such as encryption and data analysis, can block the event loop. Workarounds (worker threads or external services) add architectural complexity and require additional infrastructure.
Long CPU-bound tasks can freeze the event loop, causing delays for all other operations. This highlights why Node.js isn't ideal for heavy computation.
7. Immaturity of Some Node.js Libraries
Because of the rapid growth of the ecosystem, many packages lack rigorous testing, thorough documentation, or long-term maintenance. Using poorly maintained modules can lead to bugs, security vulnerabilities, and dependency conflicts within the ecosystem.
According to ResearchGate, many of these tiny Node.js libraries don’t do much, but still need extra work to keep everything running smoothly.
8. Ecosystem Fragmentation
A variety of libraries serve similar purposes, leading to inconsistent tooling, integration challenges, and version incompatibilities. This makes it hard to choose the right tools and creates extra work to keep everything updated and working together in larger projects.
A study in ERCIM news discovered that npm has tightly connected groups of packages. If there is a problem with one package or if the package gets removed somehow, that will easily affect many other packages, and whole systems might break.
Thinking of upgrading your app with Node.js?
Let's TalkLoading...
When to Use Node.js
‣ Real-Time Applications
As said, Node.js is perfect for chat apps, live dashboards, multiplayer games, or collaboration tools like Trello.
‣ RESTful APIs
Node.js, along with supporting frameworks like Express.js, helps build fast and scalable APIs. It is extensively adopted within microservices architectures to create modular services that are independently deployable.
‣ Streaming Applications
Node.js provides native stream modules that help developers build efficient streaming applications, especially for handling real-time audio and video data. For example, Netflix used Node.js to rebuild its website's UI layer. Netflix achieved a significant performance improvement, reducing the startup time by approximately 70% by streamlining server-side rendering and client-side delivery.
‣ I/O Bound Applications
Node.js is well-suited for applications that perform frequent I/O operations, such as database queries, API calls, or file system access. Its non-blocking, event-driven architecture makes it ideal for high-throughput systems where the application spends significant time waiting on I/O. For example, eBay uses Node.js to build scalable services that handle large volumes of concurrent I/O operations efficiently.
‣ Microservices-Based Applications
Built with Node.js, companies like PayPal and Uber have created modular, scalable platforms that are easy to manage and expand. As an example of Node.js’s ability to achieve significant business benefits, LinkedIn migrated from Ruby on Rails to Node.js for its mobile backend servers from 30 to 3 (a 90 % reduction) and saw performance improve by up to 20× faster in some scenarios, demonstrating the power of an event-driven architecture and client-side rendering strategy.
‣ Single Page Applications (SPA)
Node.js is commonly used as a backend for SPAs built with React, Angular, or Vue.js. It efficiently handles API requests, enabling fast data exchange and supporting smooth, real-time interactions on the frontend.
When Not to Use Node.js
‣ CPU-Intensive Applications
As noted above, Node.js has a limitation when executing tasks that rely heavily on CPU usage.
‣ Applications Requiring Complex Multi-Threading
As discussed above, for systems that need true parallelism, like financial engines or high-performance analytics, languages with multi-threading (e.g., Java and C#) are a better solution than Node.js. Node.js offers worker threads, but multi-threaded environments are more efficient and scale on larger systems that need concurrency.
‣ Monolithic Applications
If a company is used to building all parts of an app in a monolithic system, they may find it difficult to work with Node.js, which is designed for small, separate services (microservices). With Node.js, it becomes much harder to manage a large single codebase, deploy everything at once, and keep shared data consistent in a monolithic setup.
As IBM says, monolithic architecture can manage debugging better than microservices because it is simpler. Therefore, Node.js isn’t suitable for monolithic applications.
‣ Tasks Requiring Traditional Relational Databases with Complex Queries
While Node.js can utilize SQL databases such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, the platform is not optimized for complex joins, transactions, or stored procedures. It is possible to use these features with Node.js, but it is often less efficient than using frameworks like .NET (Entity Framework) or Java (Hibernate), which provide better support for traditional RDBMS logic.
A study comparing ASP.NET Core and Express.js (a popular web framework of Node.js) found that .NET performs better in managing MySQL operations when there are more workloads.
Conclusion
Node.js is one of the top options for web development in 2025, especially for applications that need real-time interactions. Developers can build more productive applications quickly with the non-blocking Node.js architecture that runs on JavaScript in the front-end and back-end.
Better performance, a large collection of NPM packages, reliable input/output handling, and easy integration with modern tools like GraphQL and TypeScript are some benefits of Node.js. Many developers prefer TypeScript for its strong type system that improves code quality and maintainability, especially when the projects become more complex. You can deploy Node.js applications on serverless platforms such as AWS Lambda and Azure work well with Node.js. Many popular companies like Netflix, Uber, LinkedIn, and PayPal also use Node.js.
That said, Node.js is probably not the appropriate option for CPU-heavy applications or heavy multi-threaded logic. In such cases, a different tech stack suits best. However, for most businesses and in particular, businesses that need updates constantly, fast time to market, real-time functionalities, or scalable architecture, Node.js is a great fit. When making calls to serve many users, Node.js will serve much faster API response times and comes with more significant speed and performance compared to many other platforms.
At Webandcrafts, we develop effective and reliable backend solutions and offer Node.js consulting services alongside custom development. We have helped organizations like Logos Learning, CAFS, and Middlesex University Dubai deliver reliable digital platforms tailored to their unique needs.
Being a Node.js Development Company, we have the necessary skills and expertise to develop reliable and scalable Node.js solutions. We are very well prepared to transform your ideas into reality by building a custom solution that aligns with your business goals.
Are you looking to enhance an existing project? Or are you building something from scratch? Our team will help you build what's next with Node.js. If you want to work with our experts, hire our Node.js Developers at Webandcrafts and let us create something great together!
Ready to start your next big project with us?
Let’s talkLoading...
Discover Digital Transformation
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.










