Best iOS Architecture Patterns for Your App’s Success
Listen to this article

In 2024, people spent over $1.3 trillion through apps on Apple’s App Store, more than double what they spent in 2019. As users always expect outstanding apps, smooth and responsive app performance is no longer optional; it is mandatory.
Research by AppDynamics has shown that over 80% of users stop using an application due to poor performance. There are a lot of reasons why an application performs poorly, most of which can be faults of the application’s architecture. Poor architecture leads to bugs and increases maintenance costs.
So, how do iOS architecture patterns help address these issues? Architecture patterns like MVC, MVVM, and VIPER provide structured approaches to organizing your codebase. By defining clear roles and responsibilities for each component, these patterns easily manage the complexity, reduce bugs, and improve performance. Architecture patterns can help develop apps that are easier to test, maintain, and scale. Some patterns just help developers develop their apps quicker, while others can handle complex features better. The decision in choosing what patterns to use can depend on your goals with your project, the size of your team, and future goals.
This article will detail the importance of choosing the correct iOS architecture pattern, compare some of the most common architecture patterns available, and, more importantly, how they affect the overall quality, performance, and cost of your application.
In a Nutshell
The quality of an iOS app depends on the development approach behind it. There are some iOS architecture patterns, such as MVC, MVVM, VIPER, or TEA, which can make applications easier to test, improve, and maintain. MVC is a simple and fast architecture pattern for small applications. MVVM and VIPER are better for complex or team-based projects. MVVM and TEA are even more effective with SwiftUI and iOS 16. The right architecture patterns ensure better performance, minimal bugs, and smoother updates for an application.
What Is iOS App Architecture?
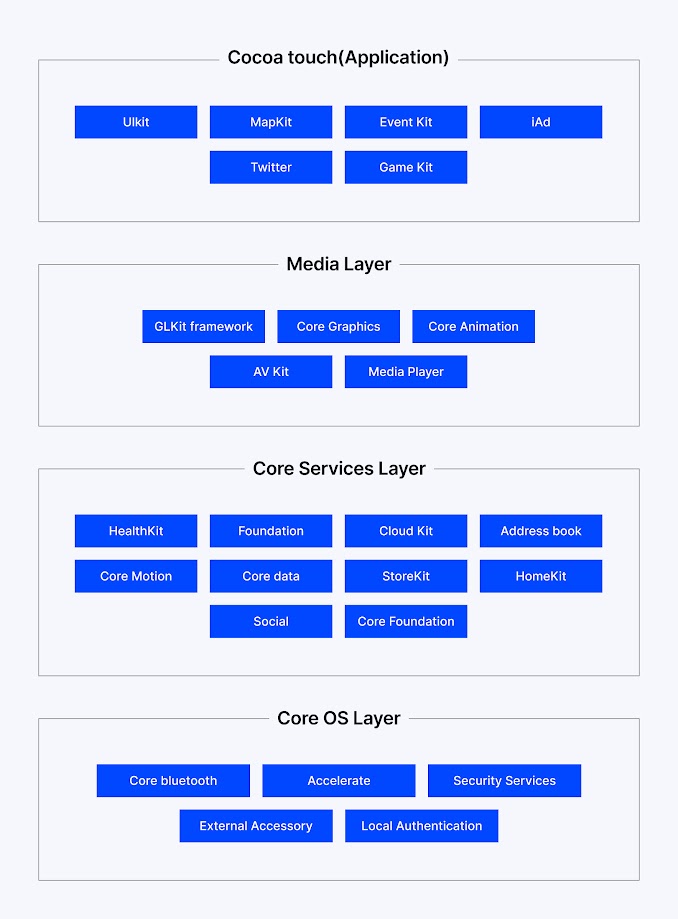
iOS app architecture is the way to organize an app's source code, components, and layers, and how they interact with each other. This is like the blueprint that provides developers with an outline to develop scalable and maintainable applications. A strong architecture not only supports adding new features and fixing bugs efficiently but also ensures performance and stability as user demand increases.
Specifically, Apple developed its iOS with a layered system architecture, which determines how apps should interact with system services, hardware, and user interfaces. Each layer has a specific purpose, and all layers work together to give a complete iOS experience.
Even Apple had to rethink its application architecture.
First, we wanted to do a hybrid architecture. Later, we realized that that approach was not going to help us achieve the quality that we want for our products.
Tim Cook, CEO, Apple.
This shows why selecting the right architecture is the foundation for building stable yet high-quality applications.
1. Core OS Layer
This is the base layer of the iOS operating system and interacts directly with the hardware of the device. It manages low-level operations such as:
- Memory management
- File system operations
- Networking
- Security services
It has the basic frameworks like Core Foundation and other system-level APIs. While developers don’t spend a lot of time working directly with this layer, understanding this layer is important for deciding how to manage performance and other system-related decisions.
For example, when a banking app uses Face ID to log you in, the Core OS Layer handles the secure access to the device’s hardware and biometric data behind the scenes.
2. Core Services Layer
The core services layer is the layer above the core OS layer, and this layer provides important system services and APIs that will be used by most of the applications. Important services include:
- Data persistence with Core Data.
- Multithreading with Grand Central Dispatch (GCD).
- Location tracking with Core Location.
- Basic networking and file handling.
This layer also allows communication between components and system-level features and is useful for building responsive and data-driven applications.
For example, when a food delivery app tracks your location in real time, the Core Services Layer uses Core Location to get GPS data and GCD (Grand Central Dispatch) to update the map smoothly without freezing the app.
3. Media Layer
The Media layer helps with rich multimedia experiences in iOS applications.
It has support for:
- Graphics rendering using Core Graphics and Metal.
- Animations through Core Animation.
- Audio and video playback via AVFoundation and MediaPlayer.
- Image processing, camera access, and more.
Apps that depend on visual content, sound, or animation, like games and video editors, use this layer mostly.
For example, when you use Instagram to record and edit a video with music and filters, the Media Layer handles video capture with the camera, adds audio using AVFoundation, and applies filters and animations through Core Animation and Core Image.
4. Application Layer (Cocoa Layer)
At the Application layer, located at the top of the stack, is where most of your app development will take place. This layer contains the Cocoa Touch framework, which provides:
- UIKit for designing UI components (buttons, tables, navigation).
- SwiftUI for declarative UI development.
- Foundation for working with data structures, dates, and strings.
- Other frameworks like MapKit, MessageUI, and EventKit.
This layer handles the app lifecycle, event handling, and user interaction; therefore, it is your primary development area (i.e., where most work takes place).
For example, when you open a weather app, you can see buttons, tabs, and animated forecasts. The Application Layer uses UIKit or SwiftUI to build the interface, Foundation to handle the date and time, and MapKit to show your location on a map.
Which iOS architecture pattern will power your next app?
Reach out to usLoading...
Why Are iOS Architecture Patterns Important for Your App?
‣ Improved Maintainability
An app with a well-organized code architecture makes it easier for developers to find, understand, and change components of the app. This limits the time spent fixing bugs or making changes, while also preventing new bugs from arising when code is modified. Studies show that developers spend most of their debugging time editing (41%) and testing (29%), with more complex bugs requiring extra time inspecting code and jumping between tasks. A clear architecture can help streamline this process and reduce that burden.
‣ Scalability for Growth
As your app continues to grow with more active users, more features, or more developers, a modular architecture makes it easier to add new components and scale easily. You can expand with new functionality without affecting what has already been built. A well-designed app can handle more users with relatively little rework, unlike an app built without considering future updates during its development.
‣ Enhanced Team Collaboration
A uniform design pattern creates a common language for developers, which lets teams work together on different modules with relatively few conflicts. A study by ResearchGate found that developers can understand and maintain code as a team with the help of design patterns, which makes team collaboration and integration easier.
‣ Reduced Bugs and Errors
It becomes easier to test, fix, and update when each part of your code has a clear purpose. This reduces interdependencies and simplifies the testing and maintenance of your application. Clear boundaries between components help here. A study found that bugs are more likely to happen when developers change code across different parts of the app, instead of keeping changes within one section.
‣ Better Performance
Good architecture assures that data flows efficiently and resource usage is optimized, which makes the apps run more smoothly and quickly. Good architecture eliminates unnecessary computations and memory overhead, thereby improving responsiveness and user satisfaction.
‣ Easier Onboarding
When new developers join your team, a well-organized architecture functions something like a road map. A study on arXiv found that developers who participated in structured onboarding programs produced 89% more high-quality code contributions during their initial period compared to those in unstructured onboarding environments.
Types of iOS Architecture Patterns
1. MVC (Model-View-Controller)
MVC is widely used due to its structure. MVC allows you to divide an application into 3 components:
As the creator of the MVC pattern, Trygve Reenskaug, once said:
Created MVC to help users manage and interact with complex data by dividing different parts of an application so that each part has a clear, specific job.
Trygve Reenskaug, creator of the MVC pattern.
Model: The data and business logic.
View: The view that renders the UI and represents the user interface portion.
Controller: The middle part that connects the Model and View, processes user interaction, and updates the View whenever necessary.
For example, if you're building a weather app with MVC. In it,
Model: Temperature information.
View: Represents the temperature shown on the screen.
Controller: Gets the data and updates the View.
Key Aspects:
- Can start and understand easily.
- Has strong UIKit integration.
- By separating the UI, data, and logic, MVC organizes the code.
- Apple provides extensive documentation to support.
- Good for quick prototypes and simple applications.
- Reduces the learning curve for most iOS developers, and it is a familiar iOS design pattern to all.
There is a downside to using MVC, as you can end up with a "Massive View Controller" when your controllers become too complicated as the app functions expand.
2. MVP (Model-View-Presenter)
MVP is the solution to the testability and maintainability issues in MVC. MVP takes MVC a step further by adding a Presenter, which takes many of the responsibilities of a Controller.
Model: Represents the data and business rules.
View: A Passive UI component that displays data and sends user actions to the Presenter.
Martin Fowler, a respected voice in software architecture, explains it like this:
The View shouldn’t do much in MVP. It just displays everything and passes user actions to the presenter, who handles the actual logic.
Martin Fowler, software architect and author.
Presenter: By coordinating between Model and View, it handles logic and makes the data ready for the View.
For example, if you have a shopping app, then,
Model: Handles product data management.
View: Displays the list of products to the user.
Presenter: Does the filtering and gives the processed data for the View to display.
Key Aspects:
- Passive view reduces complexity in the UI component.
- Presentation logic is still separated from the View and can be tested independently.
- The View and Presenter communicate via protocol (interface).
- UI logic tests can be more effective.
- Improved organisation of applications that have complex interactions with the user.
- It is more maintainable than MVC.
3. MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel)
MVVM adds a ViewModel that connects the View and Model using data binding, usually with reactive coding libraries like RxSwift or Combine.
Model: Handles the business logic and data.
ViewModel: Gets the data ready for display and contains View-related logic.
View: Changes state automatically by binding to the ViewModel.
Here’s how John Gossman, the Microsoft architect behind MVVM, describes it:
MVVM is an updated version of MVC. It is meant for modern applications where designers can handle the view and developers can focus on the logic.
John Gossman, Microsoft architect and creator of MVVM
Key Aspects:
- Supports two-way data binding only for specific frameworks like RxSwift.Supports reactive and declarative UI updates.
- ViewModel has no direct reference to the View.
- Good for dynamic and data-driven UIs.
- As the ViewModel is UI independent, testing becomes easy.
- Clean and less boilerplate code (code that is repeated in many places with or without changes) for state changes.
For example, if you have a music player app,
- Model: Stores songs.
- ViewModel: Formats the song title and playback time.
- View: Updates automatically whenever data changes.
4. MVCVS (Model-View-Controller-ViewState)
MVCVS is another pattern in the MVC family, with a component called ViewState that manages all your UI state, keeping the UI state separate from the Model.
Model, View, Controller: The same as in MVC.
ViewState: Manages temporary UI state, observed by the View and updated by the Controller.
If you have a login application that uses MVCVS,
Model: Handles user data.
Controller: Manages input.
ViewState: Tracks user interface states like “loading”, “success”, or “error” and updates the View accordingly.
Key Aspects:
- Explicit management of transient UI states (clearly handles temporary states like loading, error, or user input).
- Decouples persistent data from UI-specific conditions (keeps long-term app data separate from short-term UI behavior).
- More straightforward debugging of UI behaviors.
- More consistent UI behaviors across complex flows.
- Improved testing of view state transitions.
- Helps manage states across multiple navigation steps.
This separation of UI state is logically similar to SwiftUI’s approach of state-based interfaces. As noted in SwiftUI’s official documentation,
To store that information that changes over time, you use state, and SwiftUI updates the changes automatically whenever the state changes.
5. VIPER
VIPER splits your app into five parts to keep everything organized. This makes it easier to manage, especially in big apps used by businesses.
View: Responsible for rendering the UI and sending actions to the Presenter.
Interactor: Is responsible for business rules and data fetching.
Presenter: Responsible for handling user input and updating the View.
Entity: The data models and structures used by the Interactor.
Router: Responsible for navigation and screen transitions.
For example, if you have a food delivery app using VIPER,
View: Shows restaurant listings.
Presenter: Handles user taps.
Interactor: Fetches restaurant data.
Entity: Defines restaurant details.
Router: Navigates to the menu or checkout screen.
Key Aspects:
- Highly modular architecture.
- Each component has a single responsibility.
- Built for team-based, scalable development.
- Completely testable due to the isolation of components.
- Can support parallel work across teams.
- Best for large, complex, long-term projects.
Here’s how the Uber team recognized the value of VIPER, according to a senior mobile engineer at Uber:
As soon as our Uber iOS team crossed 100 engineers, an efficient application architecture was necessary for us to move forward. We thought about MVP, MVVM, and VIPER and chose VIPER finally because it was more modular, reliable, and easier for testing across teams.
Gergely, Senior Mobile Engineer at Uber.
6. TEA (The Elm Architecture)
TEA (The Elm Architecture) is based on the Elm programming language. It allows writing code in a functional style, where data doesn’t change (immutability) and flows in one direction. This makes apps easier to understand and maintain.
Evan Czaplicki, who created Elm, summarizes this well:
You can build applications in which data flows in one direction, thereby the application behaviour becomes more predictable and easier to test with ELM.
Evan Czaplicki, creator of Elm.
Model: Represents the state of the app.
View: Is a pure function that renders UI based on the Model.
Update: It is a pure function that accepts the current state and the action and returns the new state of the app.
Commands and subscriptions: Manages the side effects (network calls, timers, etc.) externally.
For example, if you have a to-do list app using TEA,
Model: Has the task lists.
View: Screen showing tasks.
Update: Update task addition or deletion in the list.
Commands: Handles functionalities like reminders.
Key Aspects:
- Unidirectional and predictable data flow.
- Every transition of state occurs through the Update function.
- TEA utilizes functional and reactive programming paradigms.
- Predictable and traceable state transitions.
- Can produce excellent debugging features like time-travel debugging.
- Very few side effects due to the functional nature of the TEA framework.
- Fits well into the SwiftUI declarative and state-driven design.
Need help choosing the right iOS architecture pattern?
Let's TalkLoading...
Factors to Pick for the Perfect iOS App Architecture
Understand the Problems with Source Code
Before you make a choice on an architecture, you should consider your existing or expected code structure. You should ask yourself:
- Is the codebase large and hard to manage?
- Do you have tightly coupled components (i.e., "Massive View Controller" problems)?
- Do you expect complex data flows or huge real-time updates?
- Will testing and feature upgrades be your priority?
If your app is likely to face these challenges, it's a good idea to use structured iOS architecture patterns like MVVM or VIPER. By clearly separating different responsibilities in the app, these patterns help keep your code more organized, easier to test, and easier to maintain.
Prefer the One That Improves the Code Criterion
Good software architecture improves the health of the codebase over time. Find those patterns that naturally support the following.
- Modularity: Separating your app into independent, reusable segments.
- Testability: Simplifying unit testing by isolating components.
- Maintainability: Enabling easier debugging and further improvements.
- Readability: Making your code readable for all developers who are going to get involved in the development process.
- Scalability: Supporting application growth without rewriting completely.
For example, MVVM would be beneficial for applications that involve complex UI logic, as its method supports data binding. VIPER is good for enterprise-level projects that require strict modularity.
Determine the Objective of the Design
Every application has its own business goals, and your architecture should satisfy those goals:
Use simple patterns like MVC for fast MVPs or prototypes, which provide fast development but with some initial overhead.
Use MVVM or VIPER for enterprise-grade applications where you can enforce a strong structure and ensure maintainability.
If the app interacts with multiple third-party APIs or deals with real-time data, your architecture must be able to manage complex state management and data flows effectively.
Finally, think about the future direction of your application. Will it improve significantly? Will it become a platform? Plan for appropriate architecture wisely.
Some Real-World Examples of iOS Architecture Patterns
‣ Apple’s UIKit-Based Apps
Apple's native apps, including Mail, Photos, Settings, and Calendar, typically adopt a straightforward version of Model-View-Controller (MVC) because of UIKit's natural support of the architecture for native apps. In these apps:
Controllers: Responsible for UI logic, interpreting user inputs, and updating the view.
Models: Responsible for managing the data, mostly linked with system-level services.
Views: Renders data as directed by the controller.
Apple apps are the right examples that show MVC can work really well if used in the right way. Using techniques like delegation and notifications, Apple keeps everything organized by clearly dividing responsibilities. This proves that even a simple MVC architecture can handle complex features and give users a smooth experience when the setup is done properly.
According to Apple’s developers,
MVCs clean up your code and organize it. It makes your app easier to reuse, the structure easier to understand, and makes app updation and expansion easier for the future.
‣ Uber
Uber’s Engineering team ran into serious issues when Uber’s iOS app became more complex with the traditional Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. They observed the following:
- View controllers became massive, a few with over 3,000 lines of code.
- Business logic, UI code, and navigation were all mixed.
- Making changes or adding features became risky and time-consuming, especially for large teams.
Uber moved to the VIPER architecture to fix this problem, where VIPER breaks down each screen into five clear parts. This transition helped Uber to:
Make their code more modular and easier to test.
Let different teams work on the app at the same time without causing problems for each other.
Update features faster without breaking other parts of the app.
Gergely Orosz, a former engineering manager at Uber, shared how their architecture evolved:
At Uber, we started with MVC on iOS, but as the team grew, it just didn’t scale. We tried MVVM, MVP, and VIPER, and liked VIPER the most, but it still needed improvements. That’s how RIBs were born.
Gergely Orosz, former engineering manager at Uber, Bitrise Q&A
Later, they refined VIPER further into a new system called RIBs, which made their architecture more scalable again.
Conclusion
Creating a successful iOS application is more than simply writing clean code. It begins with the selection of the right architecture. iOS design patterns are not plug-and-play solutions. Rather, they are patterns that help you make strategic and architectural decisions that will determine your app's performance and adaptability over time. Whether you are building a simple MVP or a complex and enterprise-grade solution, architecture impacts the development, collaboration, code maintenance, and user satisfaction.
From the simplicity and speed of implementation of MVC to the data-binding and reactive nature of MVVM and the modular and scalable approach of VIPER, there are differences between each one that make them suitable in different situations.
MVC is great for small apps with basic UI logic, and MVVM excels with more complex UIs and asynchronous data. In large, team-driven projects, VIPER ensures clear separation of concerns.
With the arrival of SwiftUI and Combine, the iOS development industry is moving toward more declarative and reactive architecture. These frameworks are a perfect fit with patterns like MVVM and The Elm Architecture (TEA) that promote better state management and cleaner UI code. Developers now need to choose an architecture not only based on how complex the app is but also based on new tools and how easy the app will be to maintain in the future.
With the launch of iOS 26, Apple introduced a new design called Liquid Glass and updated SwiftUI to support rich visuals. These changes make it easier to use patterns like MVVM and TEA that focus on clear structure and reusable parts.
Looking ahead, picking an architecture is not just a matter of trend. The appropriate architecture has to fit with the goals for the app, the experience of the team, and the long-term roadmap for the app. Picking the right architecture helps you to make sure your app is easy to update, works well, and can improve as user needs and technology change.
Being a trusted iOS development company, at Webandcrafts, we develop iOS apps using the latest architecture patterns like MVC, MVVM, and VIPER. Our approaches, based on modern architecture patterns, ensure excellent scalability, maintainability, and the perfect user experience for your business goals.
Our iOS developers have experience developing apps similar to Caribou Coffee, an intuitive mobile platform built for one of the leading retailers in the Middle East. Check out our case studies to learn more about our expertise in iOS development. If you're building a new iOS app or enhancing an existing one, we’re here to help bring your vision to life. Let’s collaborate and develop your next iOS app!
Wondering which architecture best fits your app’s goals?
Let's talkLoading...
- React Native vs Swift: Which one should you choose for iOS app development?
- SwiftUI vs UIKit: Which iOS UI Framework Should You Choose in 2026
- Swift Vs. Objective-C: Which is the Best Option for the 2026 iOS App Development?
- Top iOS App Development Trends for 2026
- How Much Does It Cost to Develop an iOS App In 2026?
Discover Digital Transformation
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.










