Top 10 Advantages and Disadvantages of DBMS

Businesses generate a lot of data. While the volume increases, it is necessary to have a database management system (DBMS), which helps categorize large quantities of information. According to Grand View Research, the global DBMS market was valued at USD 100.79 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.1%, reaching USD 241.27 billion by 2030.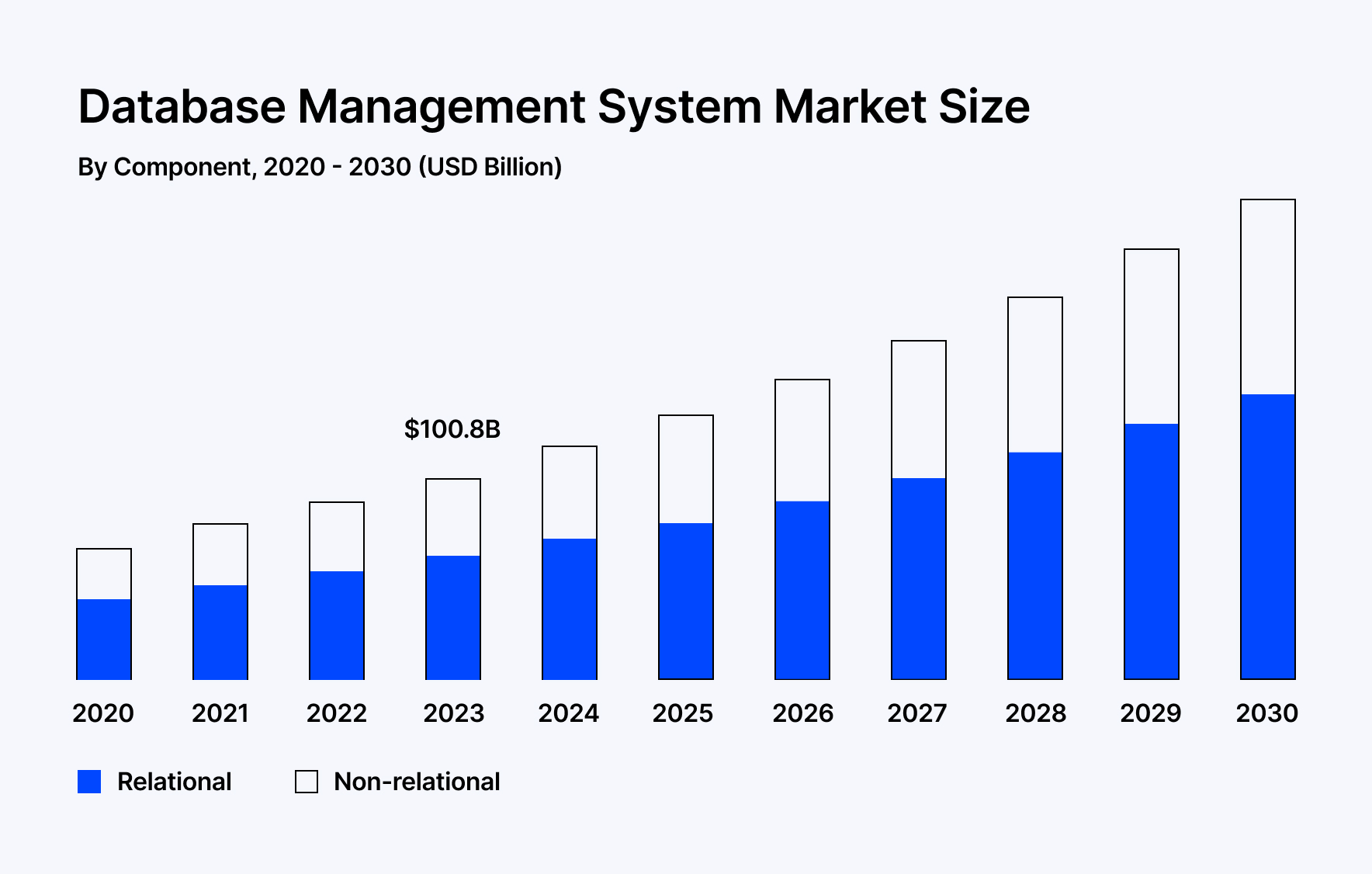 Strategically employing data in an organization leads to significant results. It creates a more productive workforce, enhances compliance with data regulations, and improves data-driven decision-making. While having all these merits in hand, DBMS has come with cons.
Strategically employing data in an organization leads to significant results. It creates a more productive workforce, enhances compliance with data regulations, and improves data-driven decision-making. While having all these merits in hand, DBMS has come with cons.
This article explains database management systems (DBMS), how they work, their important components, and their advantages and disadvantages. Read through it to get a comprehensive idea of DBMS.
What is a Database Management System?
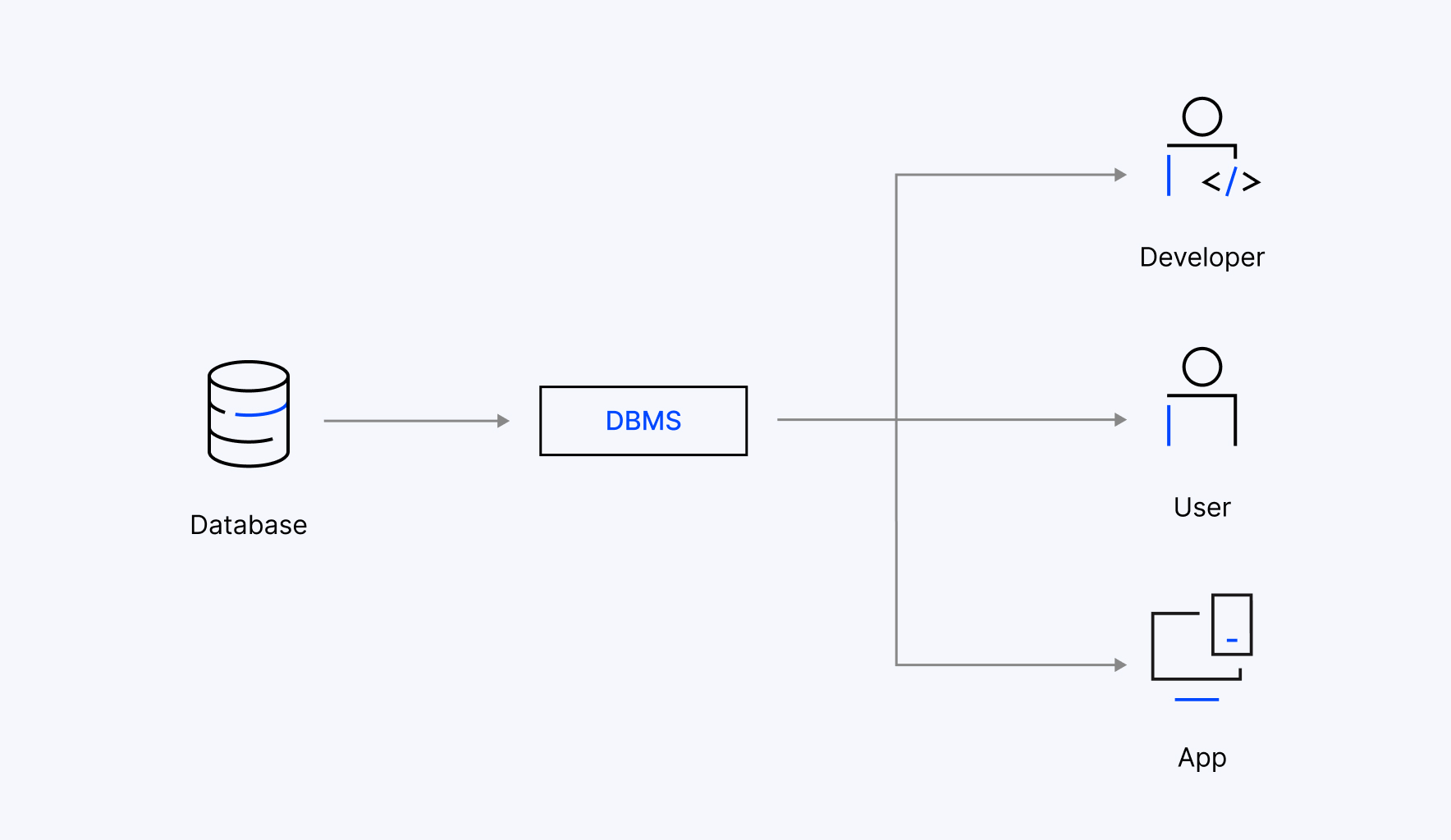
A database management system (DBMS) is software used to store, manage, retrieve, and manipulate data from a database. DBMS manages structured databases and performs operations concurrently. Oracle, MySQL, AWS RDS, Azure SQL, etc., are some of the popular DBMS tools. It is a systematic approach to handling data and finds applications in banking, social media, finance, airplane and railway reservations, among others.
The DBMS serves as a crucial link between the database and its users, which include developers, end users, and applications, by providing a secure, efficient, and organized framework for managing and accessing data.
How Does a DBMS Work?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is regarded as the interface between application programs and databases. It ensures that the data in an organization is arranged and accessible. It enables data access and management and defines the database structure.
Users are unaware of the data's storage location, as the database management system handles data requests. Developers can seamlessly exchange data using the Application Programming Interface, eliminating the need to modify programs when database changes occur.
Important Components in DBMS
Here are the key components of DBMS that you should know about:
1. Data Retrieval
The first essential capability of a DBMS is that it can retrieve data. It uses various query techniques to get data from the system.
2. Backup and Recovery
Data protection is crucial in every business. DBMS has tools to back up and restore data in case of a failure.
3. Access Control
To manage data, robust security is essential. Only permissible users can view, change, or delete data.
4. Data Storage
Data storage is where information is kept. To protect and preserve data, different methods and formats are used.
Thinking of optimizing your database with DBMS?
Reach out to usLoading...
Advantages of Database Management System
The advantages of a database management system (DBMS) include upgraded data security, seamless integration, data abstraction, less redundancy, improved data sharing, consistency and accuracy, and better organization. It also ensures efficient data access and retrieval, informs decision-making, and offers scalability and flexibility.
Let's learn more about the advantages of using DBMS and how they contribute to more efficient data management.
1. Data Security
Data has to be stored securely. The more your data is accessible to users, the more it is prone to having security troubles. You must restrict database access to only authorized users and authenticate their identities using a username and password. Access to the database should never be permitted to unauthorized individuals. Here is where DBMS comes to the rescue.
The Database Management System (DBMS) provides a superior platform for storing data while ensuring compliance with data privacy and security policies. Corporate companies commonly utilize it, investing significant capital, time, and effort to ensure data security.
2. Data Integration
A Database Management System ensures that your data is well organized and synchronized in various forms of data, and such an arrangement makes data handling easy. It also gives you a picture of how a particular organization functions. You can also keep track of how one segment of the company affects other segments. The system can also identify connections between different pieces of information and can lead to new insights and innovations.
3. Data Abstraction
The major advantage of a database is that it can provide users with an abstract view of the data. Developers use different levels of algorithms to increase the efficiency of databases. To enable users to interact with the entire system easily, developers primarily conceal these from the users through different levels of data abstraction.
4. Reduction in Data Redundancy
Redundancy in data refers to the methods used to keep duplicate data in a database. This leads to increased maintenance needs and inefficient use of storage space.
A DBMS reduces data redundancy through various techniques, and this includes:
- Normalization to organize data effectively.
- Eliminate repeated or redundant entries through data deduplication.
- Run data integrity to ensure only necessary and accurate data is retained.
5. Data Sharing
Data sharing between various departments through a DBMS is basic. Imagine it as a shared library where authorized users can borrow books. When companies update their information, it instantly becomes available to everyone who needs it. This immediate sharing of information increases collaboration and thereby avoids confusion and out-of-date information.
6. Data Consistency and Accuracy
While storing data, consistency is paramount. DBMS guarantees uniformity in storing all data copies. DBMS enforces uniform rules for all users accessing the data, promoting consistency and minimizing errors and discrepancies. Imagine it as a game where every player obeys the rules uniformly; the game will be fair and fun at the same time.
7. Data Organization
DBMS (Database Management System) employs a systematic approach to organize data in a structured way. This technique makes it easier to store, manage, and retrieve data whenever necessary. When data is organized reliably using a DBMS, it improves operational efficiency and decision-making in an organization.
8. Efficient Data Access and Retrieval
By employing techniques such as indexing and query optimization, DBMS allows efficient data access and retrieval. It also restores the database after a system failure or crash to prevent data loss. This technique used by DBMS helps in reducing the time required to process large volumes of data and ultimately improves the overall performance.
9. Better Decision Making
Database Management Systems (DBMS) make data organized, integrated, and easily accessible, and thereby enable better decisions. It also enhances data accuracy, quality, and consistency, providing professionals with the required insights on time. Moreover, DBMS streamlines data analysis and enhances information flow to help businesses understand the current trends, optimize operations, and boost overall productivity. This kind of structured, reliable data is often used to build clear business narratives for stakeholders using a Flipsnack pitch deck maker for investors.
10. Scalability and Flexibility
In database management systems (DBMS), scalability is the system's capacity to grow and accommodate an organization's expanding data requirements. It can easily handle large volumes of data, or it can scale up or down as per the requirements of an organization. It also provides flexibility in data storing, retrieval, and manipulation, and allows users to easily modify the structure and content of the database as per requirements.
Disadvantages of Database Management Systems
DBMS comes with many disadvantages, including high-cost hardware and software, complexity in implementation, the need for skilled database professionals, performance overhead for simple tasks, vulnerability to security threats, the risk of system failure affecting the entire database, frequent maintenance and updates, costly and risky migration, potential misuse of centralized data, and hidden long-term operational costs.
Let's look into these challenges to get a better understanding of how to tackle each of them.
1. High Cost of Hardware and Software
The main disadvantage of DBMS is its expense. It requires significant processing power, which involves high-speed processors and advanced hardware. Both of them are expensive and increase the cost of the entire system. Moreover, DBMS requires large amounts of fast and reliable storage along with costly software to manage and store data efficiently. The hardware and software requirements increase the initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses of operating a DBMS.
To tackle the high costs associated with a database management system (DBMS), consider utilizing open-source software, cloud-based solutions, and scalable hardware to minimize both initial investments and ongoing maintenance expenses.
2. Complexity of System Implementation
A large number of companies are using database management systems. DBMS can meet various needs and solve multiple problems within an organization. The wide range of functionalities offered by DBMS can also lead to increased complexity. DBMS is not simple software, and developers, database administrators (DBAs), designers, and even end users should have a proper understanding of it.
Serious issues, including data loss, poor database design, or even system failure, can lead to significant consequences for the organization, such as operational disruptions and poor decision-making. This requires a team with a thorough understanding of DBMS complexities, particularly when making storage, access, and structure decisions.
3. Need for Skilled Database Professionals
To maintain the DBMS, well-trained database professionals (application programmers, database system designers, database administrators, and data entry operators) are required. This will cost a sensible amount. At times, it may be necessary to employ the services of specific software development companies. Therefore, developing software requires a significant financial investment. To address this disadvantage of DBMS, invest in staff training, use user-friendly DBMS tools, or outsource tasks to reduce costs and dependency on specialists.
4. Performance Overhead for Simple Tasks
Small organizations and specific applications often design traditional file systems to deliver high performance. However, database management systems (DBMS) cannot operate efficiently in small-scale environments. Due to their complexity and resource requirements, they can be slower, resulting in reduced application speed and responsiveness.
For smaller firms, where speed and simplicity are more required, a DBMS can slow down the entire process. As performance is one of the key indicators of customer satisfaction, a system that runs slowly can impact productivity. It can also discourage adoption among developers, designers, and end users. Ultimately, a system’s performance is closely tied to its speed, and a performance shortfall can pose a significant disadvantage.
So, DBMS offers many advantages, but using it in a small-scale organization where high speed and straightforward operation are required is not the right choice. To overcome this, consider using lightweight or embedded databases, optimizing configurations, and avoiding unnecessary DBMS features for small-scale, high-speed application requirements.
5. Vulnerability to Security Breaches
If the Database Management System (DBMS) is not properly configured and maintained, it can be vulnerable to security threats. Poor management can allow access to unauthorized users, which can potentially result in data loss or theft.
To safeguard data against potential breaches, implement robust access controls, conduct regular security updates, utilize encryption, and maintain continuous monitoring.
6. System Failure Affects Entire Database
Database failure is another major disadvantage of a database management system. It demands regular maintenance and constant power. The data stored in a Database Management System is centralized, and if the server fails, the entire system will collapse. This can negatively impact the organization.
To address this, it is recommended to implement regular backups, utilize redundant servers, and adopt failover strategies. These measures will help in ensuring data availability and minimizing downtime during unexpected database crashes or power outages.
7. Frequent Maintenance and Updates Required
Now, DBMS frequently gets vendor updates to enhance its functionality and security. However, these frequent updates often require hardware upgrades to ensure compatibility and performance. Such actions can lead to additional or sometimes unnecessary expenses for organizations.
Moreover, every update comes with new features and commands. It necessitates constant training for the database management staff, which can be both time-consuming and challenging. Updates are essential for enhancement, but they can also induce both operational and functional complications.
Some effective ways to deal with frequent DBMS maintenance and updates include scheduling updates during low traffic hours, using scalable hardware, automating patches, and providing regular staff training to reduce downtime, costs, and operational disruptions.
8. High Cost and Risk of Data Migration
Data migration in a database management system can be both costly and risky. Moving large volumes of data requires specialized tools, trained professionals, and significant downtime. This can add to the overall expense.
Apart from that, there are some potential risks, which include data loss, corruption, or incompatibility during the process. These issues can disrupt business operations and lead to potential compliance issues. To avoid these issues, thorough planning, rigorous testing, and a proactive approach are required.
9. Potential Misuse of Centralized Data
A centralized database in a DBMS offers only streamlined access and control. But it is also vulnerable to various risks and misuse. Storing all the data in one location can lead to unauthorized access or security breaches that compromise sensitive information across the entire organization.
If proper access controls and monitoring are not in place, cybercriminals may exploit the system for personal gain or malicious intent. Centralized systems are more prone to manipulation, theft, or accidental data loss. For monitoring, strong security protocols, regular audits, and user access management are essential to prevent misuse and safeguard the integrity of centralized data.
10. Hidden Long-Term Operational Costs
Database Management Systems (DBMS) incur hidden long-term operational costs that arise from various factors, in addition to the initial software and hardware expenses. These costs may include increased operational expenses due to inefficient data processing, lost productivity from troubleshooting data issues, reduced customer satisfaction, and lower profit margins. Additional costs can stem from database license fees and infrastructure expenses, as well as the need for specialized DBA skills.
To address hidden long-term DBMS costs, organizations should enhance performance, automate tasks, educate staff, embrace cloud solutions, and conduct frequent cost analysis to ensure effectiveness, reduce costs, and maintain productivity.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, DBMS can be called the need of the hour. It serves as the backbone of several advanced technology practices such as data science, data modeling, and machine learning. A database management system turns data into a useful resource by centralizing data management, strengthening security, and enhancing data integrity and accessibility. Along with its advantages, DBMS has its drawbacks. No technology is perfect, and developers are working on creating different types of DBMS to make them more suitable for every organization.
Looking to take your database performance to new heights? Webandcrafts (WAC) creates high-performing, data-driven solutions that are tailored to meet your business requirements. From enhancing database efficiency to creating scalable applications, we are committed to supporting your digital transformation at every stage. Let’s talk!
Wondering if DBMS is the right choice for your business?
Let’s talkLoading...
Discover Digital Transformation
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.










