Web 2.0 Vs Web 3.0: What’s the Difference?

- History and Evolution of the Web
- What is Web 2.0? A Detailed Definition
- Features and Benefits of Web 2.0
- What is Web 3.0? A Detailed Interpretation
- Features and Benefits of Web 3.0
- Examples of Web 3.0 Technologies
- Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0- A Quick Comparison
- Web 2.0 Vs Web 3.0- Which is Better for Your Business?
- Ensuring a Smooth Transition into a Web 3.0 Business
- History and Evolution of the Web
- What is Web 2.0? A Detailed Definition
- Features and Benefits of Web 2.0
- What is Web 3.0? A Detailed Interpretation
- Features and Benefits of Web 3.0
- Examples of Web 3.0 Technologies
- Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0- A Quick Comparison
- Web 2.0 Vs Web 3.0- Which is Better for Your Business?
- Ensuring a Smooth Transition into a Web 3.0 Business
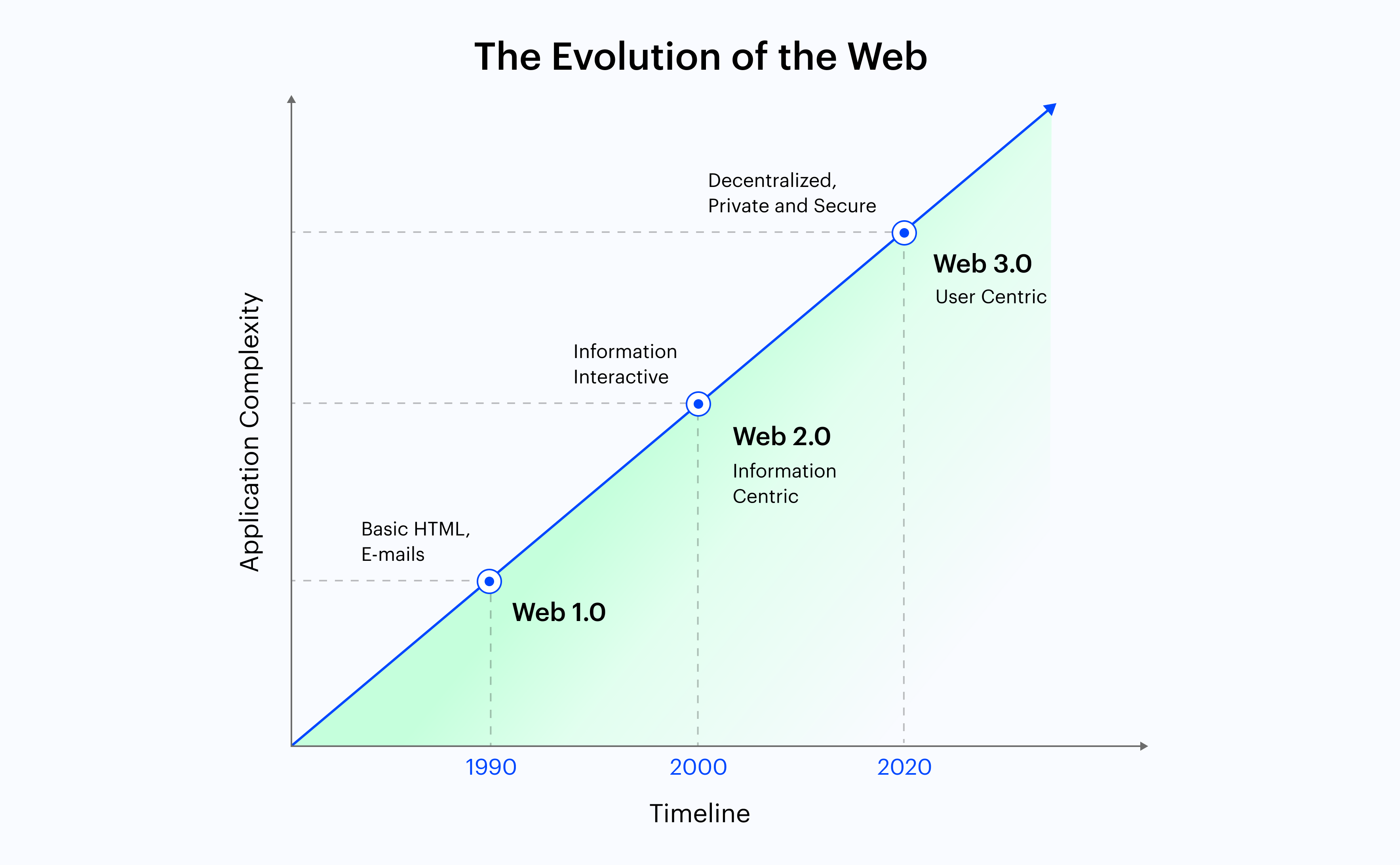
The conventional iteration of the World Wide Web (WWW) was Web 1.0, which created the blueprint for the present Web and laid the foundation for the evolved version of Web 2.0. The introduction of Web 2.0 enabled a better user-centric online experience.
Now we enter a new phase of web technology with the advent of the Web 3.0 version. Web 3.0 offers a highly interconnected and smarter online experience. With artificial intelligence and machine learning, Web 3.0 understands user requirements, facilitating an in-depth, personalised experience.
What is the difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0? While comparing these web versions, both offer exceptional advancements but differ based on key features, functionalities, and the possibilities they have for the future. In this blog post, let’s learn more about the web versions, Web 2.0 vs. Web 3.0, and their detailed comparisons.
History and Evolution of the Web
Web 1.0
The internet has undergone a huge transformation since its inception. The first version of the Internet, Web 1.0, started with a read-only type of web content. The web has continuously evolved in its usability and how we interact, from static pages to interactive platforms. Let’s dive into the two significant eras of the web we have experienced.
Web 2.0
Emerged in the 2000s, this version focused on user-centricity. It focused on a dynamic platform for social interaction and content creation.
- User-Generated Content: Focused on User-Generated Content, which includes social media platforms, blogs, and wikis to let users create and share the content.
- Social Networking: Platforms, like Facebook and X, connected people worldwide and improved online communication.
- Cloud-based services: Applications such as Google Drive and Gmail give better access to data and tools from any device.
- Interactivity: Web applications became highly engaging, responding to the user’s inputs and facilitating real-time communications.
However, the power resided in only a few large companies controlling user data and platforms. User data collection and monetisation strategies raised concerns about online manipulation. Content creators also needed help to gain fair compensation for contributions on many platforms.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0, in its early stages, focuses on addressing some of the drawbacks of Web 2.0. It provides a detailed, secure, and user-controlled Internet.
- Decentralisation: Blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks emphasise the distribution of power and data storage that minimises the dependence on centralised entities.
- Semantic Web: Semantic data structures and AI will let machines define the meaning of web content, which leads to a highly intelligent web.
- User Ownership: Users will exercise high control over their data and digital assets, driven by technologies such as tokenisation and blockchain.
- Web Monetisation: Advanced economic models are evolving to enable creators to directly monetise the content and platforms to fairly share the revenue.
Web 3.0 is evolving to revolutionise industries like social media with decentralised social platforms that prioritise user privacy and data ownership. Decentralised finance provides possibilities for peer-to-peer financial solutions and democratised access. Creators can also benefit from the new ownership and monetisation opportunities the version offers.
What is Web 2.0? A Detailed Definition
The current generation of the Internet presently in wide use globally is Web 2.0, which has transformed the Web and allied industries. This web version has made it very simple for users to gather, generate, and distribute significant amounts of information with a single click. Many new applications are introduced to the app store every day. Nevertheless, phones have an in-built camera that generates images unlike any other genuine cameras on Web 1.0 could imagine some years ago.
Web 2.0 technology enables users to develop content and distribute information across global networks. Social media channels like Facebook and Instagram, blog posts, podcasts, video streaming applications, and social bookmarking are examples of Web 2.0 platforms. This phase was also known for the convenience of sharing music and video snippets.
Features and Benefits of Web 2.0
- ‘Guide on the side’ approach: Web 2.0 dynamically edits or changes the content rather than a top-down approach of simply reading the content.
- Change of concept: It changed the ‘read-only’ approach to a ‘widely read and write’ approach over the web.
- Better user interaction: With Web 2.0, you get a perfect platform base that facilitates better user interaction compared to the previous version.
- Great content delivery: It changed the notion of passive consumption and content delivery to engage actively in building, sharing, and fostering collaboration.
- Cost-effective solution: It brings more workforce to the accounts at a reduced cost to encourage a high rate of participation in idea sharing and projects.
What is Web 3.0? A Detailed Interpretation
Web 3.0 is an evolving Internet version that enables users to view, write, and interact with content. The brief answer to what is Web 3.0 lies in its “read-write-execute” methodology. It comprises machine-to-machine communication and the use of dynamic applications. Web 3.0 connects decentralised data sources to offer a swift and individualised user experience, where the metaverse is being developed.
In this version, computers can analyse data like humans and intelligently manage relevant content that follows users’ needs. Web 3.0 is a decentralised Internet that utilises blockchain technology to enable data protection. Rather than the computer giants who manage the platforms, it provides consumers with stakes in applications and platforms. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and semantic web are used in Web 3.0 technology to facilitate the execution of the phase.
Computer systems gain the support of the semantic web in analysing and interpreting the context and meaning of the information, which helps end users receive the most precise result. Though platforms like Twitter and Facebook ruled Web 2.0, artificial intelligence services and DAppsWeb fuel 3.0 tech companies. Cryptocurrency tokens, such as Web3 tokens, power up the DApps.
Features and Benefits of Web 3.0
Connectivity:
Web 3.0 lets information be more connected using semantic metadata. As an outcome, the user experience grows to a high level of connectivity that manages all the available information.
Improved Privacy:
This version is designed to give more control to users over their data and privacy. Using blockchain technology, users can keep the data secure and avoid unauthorised access.
High Efficiency
Web 3.0 has faster transactions compared to Web 2.0. This is because it doesn’t need intermediaries like payment processors and banks.
Innovation
Web 3.0 is expected to create new types of services and applications that were impossible in the previous version. Some of the areas to explore are social networks, virtual reality experiences, and decentralised marketplaces.
Trust:
Blockchain technology lets users trust that their information is secure and transactions are transparent.
Ubiquity:
Multiple applications access the content, and each device is connected to the web, where the services can be utilised everywhere.
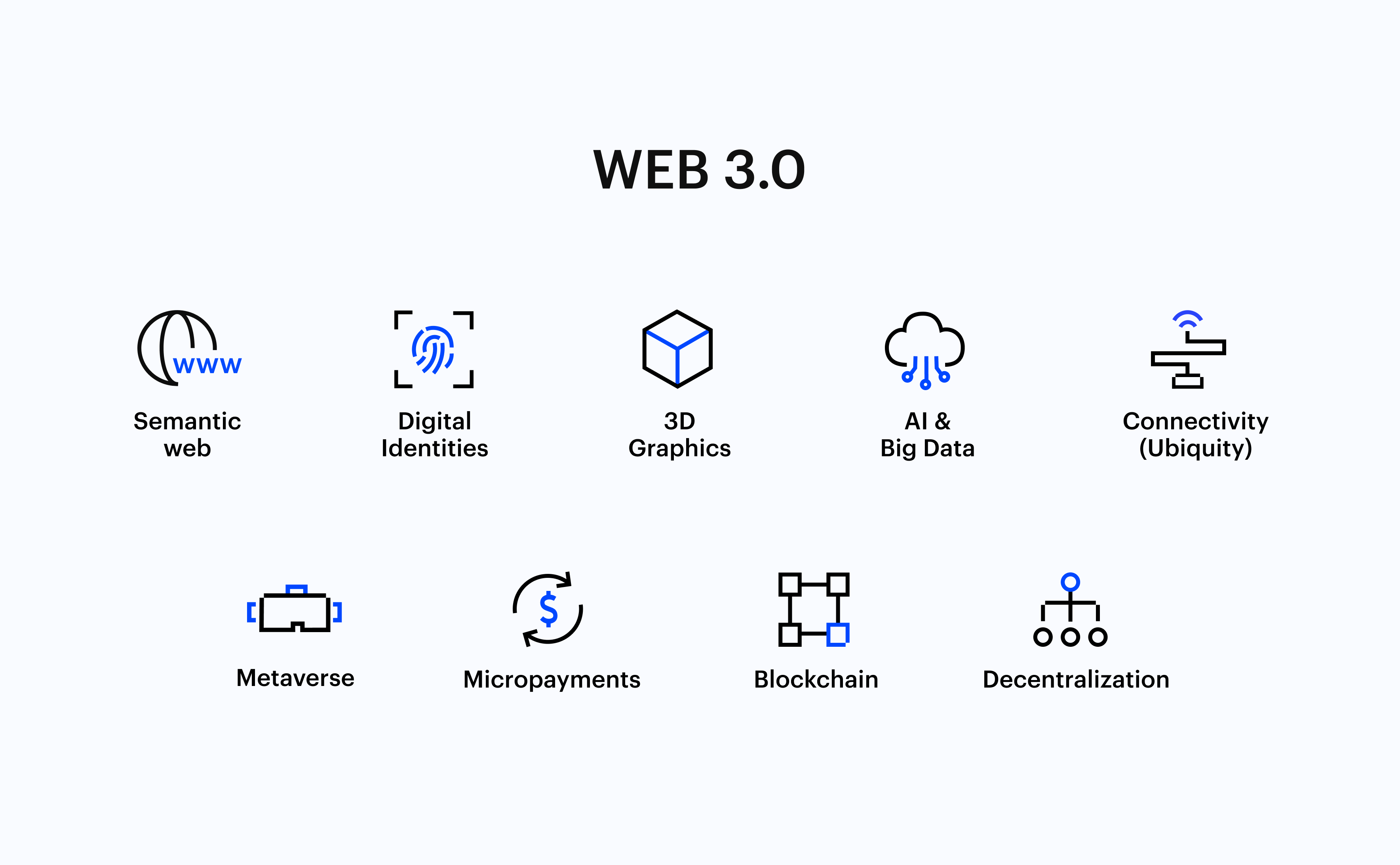
Examples of Web 3.0 Technologies
- Semantic Web: The semantic web is the latest evolution of the web. It enhances web technologies in high demand to develop, share, and connect content with the help of search and analysis, depending upon the capability to convey the meaning of words, instead of keywords or numbers.
- Artificial Intelligence: Integrating the capabilities of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Web 3.0 lets computers distinguish information like human beings to bring in faster and more relevant results. This enables them to become smarter and fulfil the user’s requirements.
- 3D Graphics: In Web 3.0, three-dimensional design is largely used for websites and services. For example, e-commerce, computer games, and geospatial contexts are examples that utilise 3D graphics.
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): DLT provides users with a database that is impossible to hack, from which the user can add value to the content or information they virtually own. Smart contracts and eliminating a middleman let you generate more opportunities for everyone.
- Blockchain: It is a decentralised method to store and share information, making it convenient to engage in financial transactions. Bitcoin is a real-time example of blockchain technology. The digital currencies use blockchain technology to track transactions transparently and securely.
- Virtual Reality: Web 3.0 technology has already transformed the way we face the world. VR is a completely immersive digital environment that enables users to interact with a simulated world. Gaming is a real-time example of VR, where video game developers use it to create highly engaging and immersive gaming experiences.
- Internet of Things (IoT): This is yet another Web 3.0 technology, which is a network of devices linked to the Internet. It lets them share data and interact with each other. Smart homes are real-life examples of IoT technology. It automates and controls everything, including lighting, temperature setup, security systems, and appliances.
Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0- A Quick Comparison
Aspect | Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Model | It involves a centralised Internet where service providers and corporations hold the power. | It focuses on creating a decentralised Internet where power is distributed between users. It uses blockchain and peer-to-peer networks for transactions, communications and data sharing. |
| Technologies | Conventional web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. | The latest technologies, such as blockchain, IPFS (Inter-Planetary File System), and peer-to-peer networks for decentralisation. |
| Application | Communicating with centralised platforms like social media, e-commerce, and online services. | Participating in decentralised networks and applications that let users directly interact with services, exchange value, and manage the network without depending on intermediaries or any authority. |
| Semantic Processing | Basic know-how of content and structure but limited semantic and context analysis among various data points | Improved knowledge of context, meaning, and in-depth intelligent data analysis that enables systems to perceive the meaning, context, and relationships. |
| Data Security | It depends on security measures implemented by platforms and service providers that secure user data and avoid unauthorised access. | It emphasises data security through cryptographic methods, decentralised storage mechanisms, and a distributed consensus approach, thus minimising single points of failure and improving data security. |
Web 2.0 Vs Web 3.0- Which is Better for Your Business?
While we differentiate Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, the former is taken as a base for the latter to evolve. The nature of your business determines the adoption of the right web version. Let us explore the comparison to analyse this better for an informed decision.
Ensuring a Smooth Transition into a Web 3.0 Business
Whether you are a startup or a well-established business that is trying to integrate the features of Web 3.0, you need to integrate the right set of AI and ML tools to take it to the next level. By partnering with a web development company that offers the right set of technology resources and expertise, you can ensure a quick transition to the latest web version.
At WAC, we offer the best digital assistance and provide an upgrade to the technical aspects with a smooth transition of your services to Web 3.0. As a leading web development services company, we offer the best digital solutions, including web app development and mobile app development, to ease your company’s journey towards improved technology.

Expert Web Development Services
Creating solid digital presence and enhancing brand value through web-based products
Discover Digital Transformation
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.










