Types of Ecommerce: Business Models & Marketing Strategies

Ecommerce has become an indispensable factor that redefines business ideology with a significant transformation. In 2023, global retail ecommerce sales hit 5.8 trillion USD, which is expected to see 39% growth and surpass 8 trillion US dollars by 2027.
Let’s think of ecommerce from a business perspective. Ecommerce offers businesses many features—marketplaces, dropshipping, and subscription models, to name a few. Choosing the right model that suits your brand and building a successful marketing strategy are the keys to your business's growth.
Are you looking to generate sales and customer satisfaction with the right ecommerce business model aligned with the nature of your business? This blog is an eye-opener to the various types of ecommerce business models and the proven marketing strategies that can make your online store a huge success.
Why is Ecommerce Gaining Importance?
Ecommerce lets online store owners scale their businesses and increase profits. By using an ecommerce business model that resonates with your brand, you can enhance the profitability of your business. Let’s take a glance at some of the benefits of ecommerce business models:
Low Operating Costs & Increased Profits
Online storefronts reduce operating costs when compared to brick-and-mortar stores, as they offer automation of checkouts, payments, billing, inventory, and different operational activities. Also, with a focus on a huge customer base and the convenience of shopping, ecommerce offers businesses a great increase in revenue.
Quickest Sales Process
Ecommerce helps shoppers spend less time on purchases. Consumers can browse through the digital site catalogue to make orders. It becomes easier to receive orders and dispatch goods swiftly.
Cost-effective Marketing and Advertising
Marketing products is easy with ecommerce. You don’t require conventional hiring of sales marketers to encourage your brand’s outreach. You can accommodate various marketing strategies like Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), Content Marketing, Social Media Marketing & Management, customer loyalty programs, or even run paid ads to drive traffic and connect with customers faster.
Unlimited Reach
Ecommerce platforms help you enhance the brand’s reach. Millions of people across the globe access your website. A high reach contributes to an increase in sales.
International Transactions
You can reach a huge audience globally with ecommerce as it allows you to implement global sales of your products. Amazon, for instance, ships products to more than 100 countries worldwide.
Types of Ecommerce Business Models
1) Business-to-Consumer Model (B2C)
The B2C ecommerce business model is the most prominent classification of ecommerce where a business sells products directly to consumers. B2C is widely used to define every business that sells goods to the consumer market, which includes:
- Manufacturers selling products via a brick-and-mortar store or a website
- Consumer service providers
- Retailers that source a wide range of products targeting consumers
Some examples of B2C businesses include BestBuy, Walmart, and Amazon. They resell the products of other companies through ecommerce websites.
Adidas and H&M are examples of businesses that use the D2C model in ecommerce, by selling their products to consumers. Certain B2C companies sell a combination of their own and the other brand’s products—for instance, UK-based online clothing retailer ASOS.
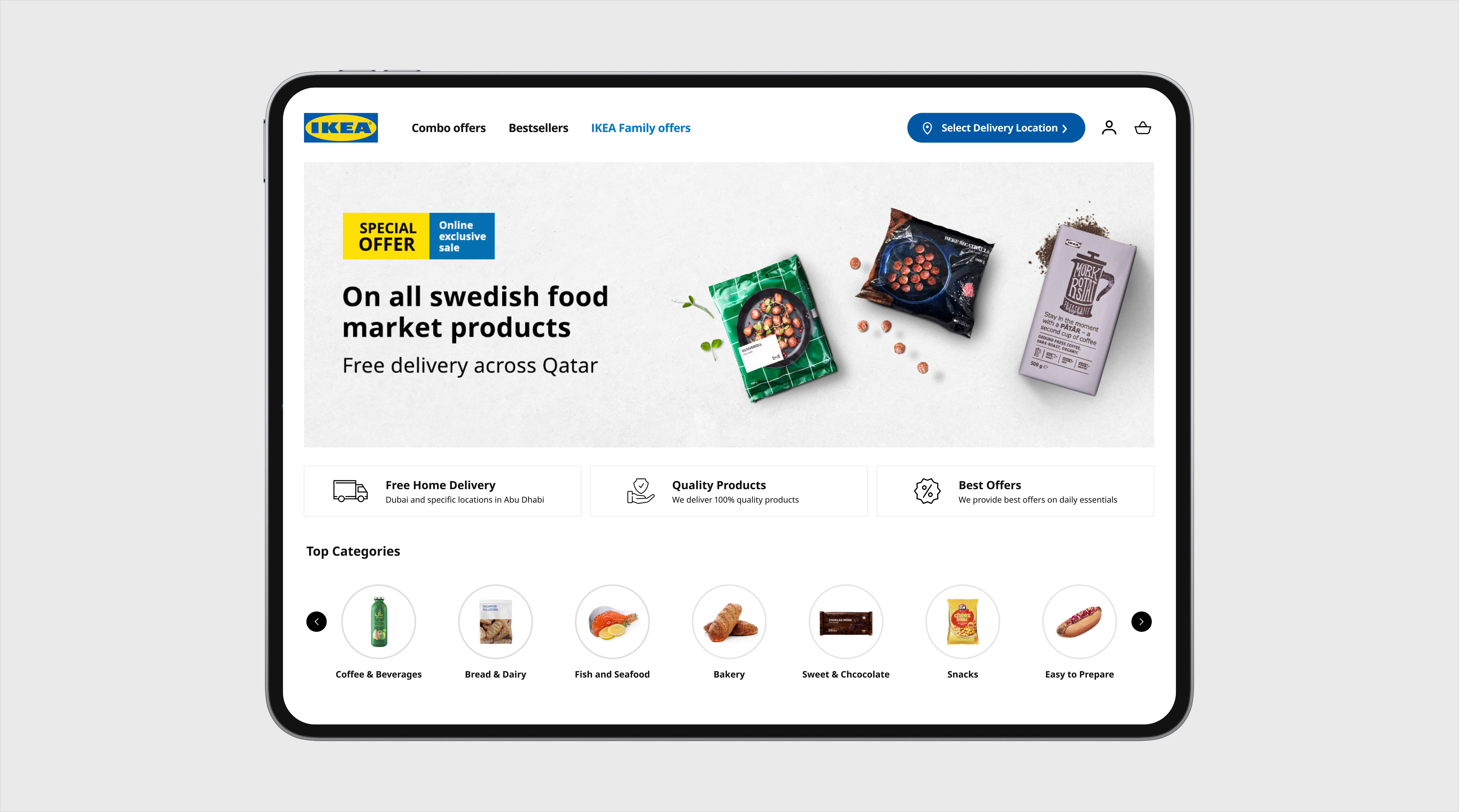
It is significant for B2C ecommerce businesses to have the following:
- High transaction volume
- Short sales cycles (the time taken to attract a prospect and let them complete a purchase)
- Reduced average transaction value
The B2C category utilises various revenue models that include:
- Dropshipping: Sellers display the other brand’s products in digital storefronts. When a consumer buys, the seller purchases the item from a third-party supplier at a low cost that enables shipping straight to the customer, in which the process is quite automated.
- Subscription services: Customers make recurring payments to avail of an ongoing service or a regular subscription. Spotify, YouTube Music, etc. are examples of B2C subscription services.
- Pre-owned or refurbished goods: The sellers source used stock they fetch from other companies and consumers. For instance, a business that sells refurbished products to consumers.
The B2C ecommerce model gives entrepreneurs easy access and the startup costs are less than opening a physical store. This is why competition can be difficult.
2) Business-to-Business Model (B2B)
B2B is one of the most widely used ecommerce business models, where businesses sell products or services to other businesses. B2B companies can either sell directly to end users or sell to businesses, which again resell the products to other consumers or companies.
For instance, Trello is a project collaboration tool and a B2B ecommerce business that sells to businesses. Also, Conversely is an auto parts manufacturer that supplies automobile factories, an example of a B2B business that sells products to other companies.
Compared to B2C purchases, B2B transactions have:
- Longer sales cycles
- High transaction values
- Increased recurring purchases
Subscription models are well-known among B2B ecommerce firms, particularly software vendors. Sellers get predictable and regular income, while buyers can manage cash flow by spreading purchase costs.
B2B commerce businesses also use a white labelling business model, where the online business sells a product for rebranding and reselling. The reseller markets it to other businesses or consumers as their own.
3) Business-to-Administration Model (B2A)
The B2A ecommerce model lets businesses market and sell products to public administrations or government organisations. These could be federal, state, county or local organisations. For instance, OpenGov is dedicated to selling software to local government agencies.
Many B2A transactions begin with an RFP, i.e., a Request for Proposal. In this model, a government agency lets businesses pitch their products or services to them to bid for a contract. B2G companies usually experience long sales cycles, strict compliance standards and huge transaction values.
B2A ecommerce models are ideal for companies with niche offerings and great marketing. Additionally, longer government contracts ensure high financial security and predictability. However, the sales process can be low and most competitive with the intervention of government bureaucracy.
4) Consumer-to-Consumer Model (C2C)
C2C defines business transactions that involve two or more consumers. It also refers to a provider who manages these kinds of online transactions. For instance, when a person sells a bike to another person, this is a C2C business model.
Online marketplaces like eBay and Facebook Marketplace are examples of C2C ecommerce platforms. A third party usually facilitates a C2C sale by handling the transaction details in exchange for a commission and bringing direct sellers and potential buyers together on favourable terms.
With the C2C ecommerce business model, buyers can find reasonably priced products or services and sellers can gain margins higher than traditional buying methods.
5) Consumer-to-Business Model (C2B)
The C2B ecommerce model engages consumers in selling products and services to companies. Sometimes, the company will be the end-user. For instance, an individual who sells an image to a newspaper makes a C2B transaction. This is because when a newspaper publishes an image, they are also the end users of the product.
In another case, the company that purchases the consumer’s goods might resell them. For example, considering Shutterstock, the image library buys images from the contributors to sell to other businesses.
Influencer networks also manage C2B transactions. They connect businesses with consumers, who are popular across social media. These consumers then sell the brand’s access to their followers and they promote the brand’s goods and services for a payment.
6) Consumer-to-Administration Model (C2A)
The C2A model involves transactions between consumers and government agencies. The C2A ecommerce model is a company that streamlines these transactions. Utility companies give businesses and homeowners direct access to government-sponsored energy solutions, for example, Dominion Energy. The company ensures reliable power and gas delivery and lets customers manage their services.
C2A ecommerce businesses simplify the administrative and payment processes by empowering consumers. They offer a choice of products and create healthy competition that minimises prices.
Ready to create your eCommerce store?
Let's get startedLoading...
Best Marketing Strategies for Ecommerce Brands
Effective ecommerce marketing minimises acquisition costs, enhances customer experiences, and improves brand awareness. Now that we have discussed the various categories of ecommerce business, let’s quickly explore the types of ecommerce marketing strategies you can use to engage and grow your customer base.
1) Search Engine Optimisation
SEO supports ecommerce efforts by enhancing the website and the online store's visibility on SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages), which helps attract potential customers. The objective is to rank at the top of search results with the keywords ideal customers use.
For instance, if a popular brand ‘XYZ’ ranks high for the search term ‘used cars’, this means people who search for used cars will see and be more likely to click the ‘XYZ’ page first.
Different factors contribute well to the search performance of your ecommerce site. The optimisation process can be classified into four tasks:
- Keyword Research: Find the product-related keywords your customers might use in search queries. Keyword research tools and website analytics can help with this.
- Site Architecture: A neatly organised site structure helps Google effectively crawl your store’s pages.
- On-page SEO: Optimise the meta title tags, headings, images, meta descriptions, internal linking, and markup, which lets search engines analyse your content better.
- Technical SEO: Improve the website’s technical elements that make it easier to crawl and index, boosting its visibility and performance on search engines.
Also, remember that Google prioritises high-quality content that fulfils the search needs of every user. While algorithms are important, the human experience should be the priority when planning and creating product content.
2) Performance Marketing
Performance marketing has become an inevitable tool for businesses that wish to elevate their online presence and improve sales. This data-driven approach generates measurable results and lets companies optimize marketing efforts to increase Return on Investment (ROI). The advertisers pay marketing companies or advertising platforms for particular actions adopted by the target audience. These actions could be clicks, impressions, sales, leads, and app installs.
Here are the key performance marketing strategies for ecommerce:
- PPC or Performance Marketing: PPC is the pillar of performance marketing for ecommerce. It includes Search Engine Advertising, in which platforms such as Google Ads and Bing Ads enable businesses to display ads in search results. Another tool is Google Shopping Ads, which is highly effective for ecommerce, where ads display product images, reviews, and prices in the search results. Social media advertising is yet another approach, where platforms such as Facebook and Instagram offer PPC options with the best targeting capabilities.
- Retargeting/Remarketing: In this strategy, the ads are shown to users who have already previously interacted with your website. In this strategy, you can use platforms such as Facebook and Google Ads, or specialised retargeting services. Also, creating custom audiences as per the user behaviour, such as cart abandonment, product views, etc., is helpful. Measuring click-through and view-through conversions is also part of the strategy.
- Social Media Advertising: While usually used for brand awareness, social media can also be used for performance marketing in terms of catalogue sales campaigns, shoppable posts for Instagram or Facebook, tracking engagement rates, click-through rates, and conversions, and utilising user-generated content to enhance credibility and conversion rates.
To measure the success of performance marketing, paying attention to the following metrics is necessary: - Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Measures the revenue earned per dollar spent on advertising.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): The cost to acquire a paying customer using a particular marketing channel.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who make a desired action, for instance, a purchase.
- Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount customers spend per transaction.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The overall revenue a business can earn from a customer account.
Implementation of a successful performance marketing strategy demands establishing clear business goals, choosing the right channels, using tools such as Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, etc. for performance measurement, continuous A/B testing of campaigns and optimisation based on data, and optimising website and checkout processes for conversions.
3) Content Marketing
Ecommerce content marketing means the creation and distribution of useful and relevant content. Consider things such as blogs, video posts, and infographics. The content helps online brands build and maintain the interest of their audience.
Content marketing improves website traffic, drives qualified leads and grows the brand's image. All these are crucial to thriving in the ecommerce industry.
Other content marketing formats are:
- Emails
- Newsletters
- Ebooks
- Podcasts
- Social media posts
Consistently delivering valuable, reliable and relevant content also helps to gain topical authority. This measures your site’s expertise on a particular subject—something Google takes care of while ranking content. Your key to increased ROI is a carefully strategic approach.
A solid content marketing strategy is designed with particular goals in mind, has clear performance indicators and involves a procedure for iterative improvement.
4) Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing is the technique of using social media to grow a brand’s audience, enhance its reputation and grow revenue. It is particularly useful for B2B and B2C businesses. Social media platforms like TikTok, Facebook and Instagram let brands connect with customers directly.
You can use this connection to:
- Answer customers’ questions
- Share relevant and helpful content
- Show the relatable side of your brand
All these actions contribute to the trust that encourages people to follow, buy from, and be loyal to the business. With social media marketing, most platforms are free to use, so you can begin building your following easily.
Social media advertising helps raise brand or product awareness quickly. Most channels include ad platforms that let you target users according to their gender, demographics, interests, languages, etc.
Looking to market your eCommerce site?
Get help nowLoading...
Tips for Improving Ecommerce Customer Experience
1) Deliver Personalised Ecommerce Experiences
Personalisation plays a major role in delivering a seamless user experience. By custom-tailoring the shopping experience to meet individual requirements, you resonate with the in-person shopping experience online, which raises recognition and value among the customer base.
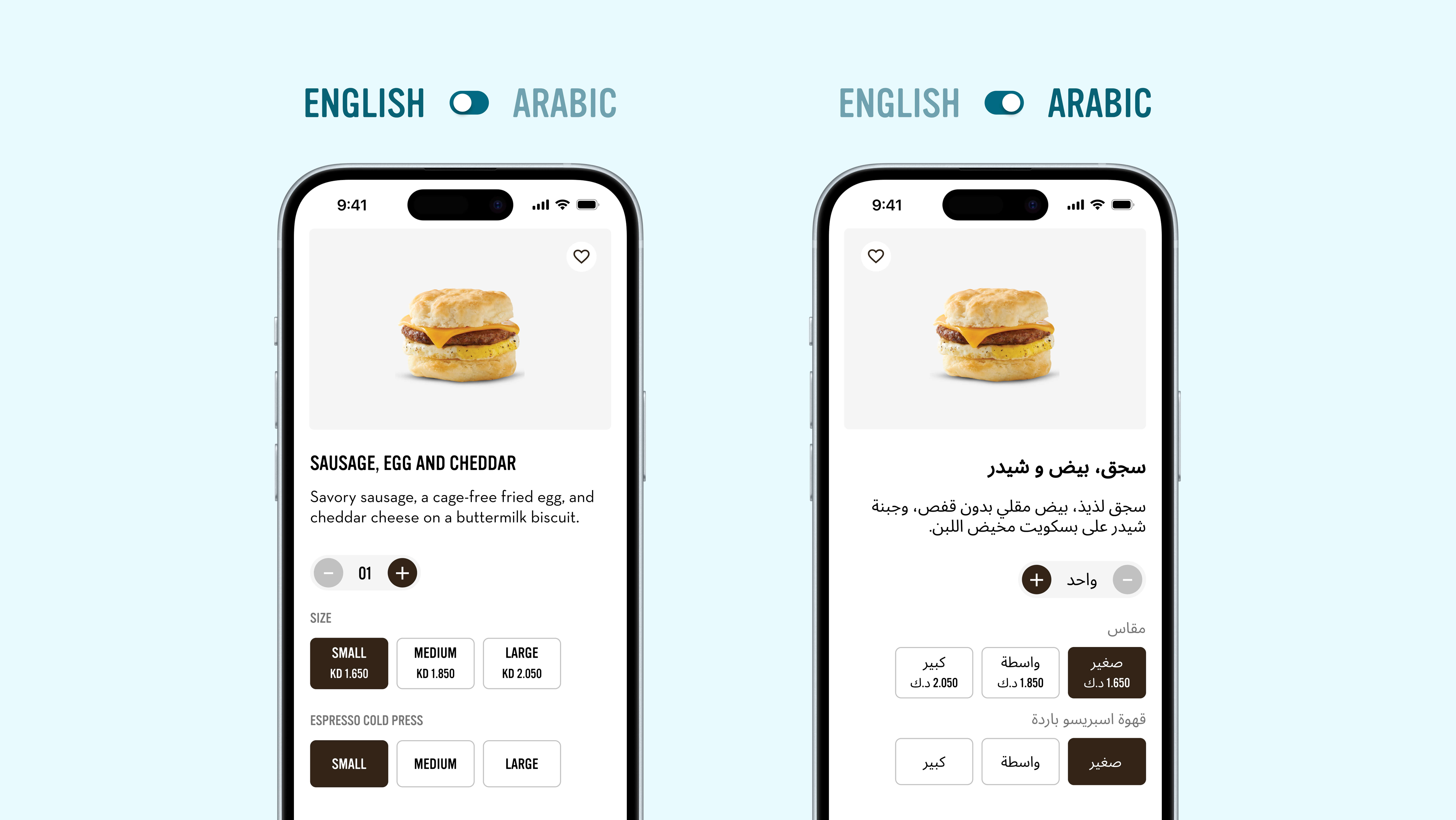
Ecommerce personalisation ranges from product recommendations based on past purchases or showing content relevant to the customer’s geographic location to sending personalised emails according to the user's behavioural patterns.
The possibilities of ecommerce evolve, and many advanced solutions are taking shape to trigger the potential of personalisation. WAC Commerce is a high-value Adobe Commerce extension with the power to deliver personalised ecommerce experiences to customers and businesses alike. In addition to the power of driving online storefronts, it has extended ecommerce functionalities like advanced search, personalised recommendations, AI-enabled similar products, an order management system, advanced analytics, etc. for a custom ecommerce experience.
Wondering how WAC Commerce can enhance your store?
Learn MoreLoading...
2) Adopt a User-Friendly Website Design
A user-friendly website should be made as simple as possible to let customers find what they should learn about what you offer and make a hassle-free purchase. Responsive design is the best way to ensure your website functions well across multiple devices, particularly considering the significance of mobile shopping. An intuitive and clean website layout helps with ease of navigation, offers fast loading times that scale the user experience and helps in the retention of site visitors.
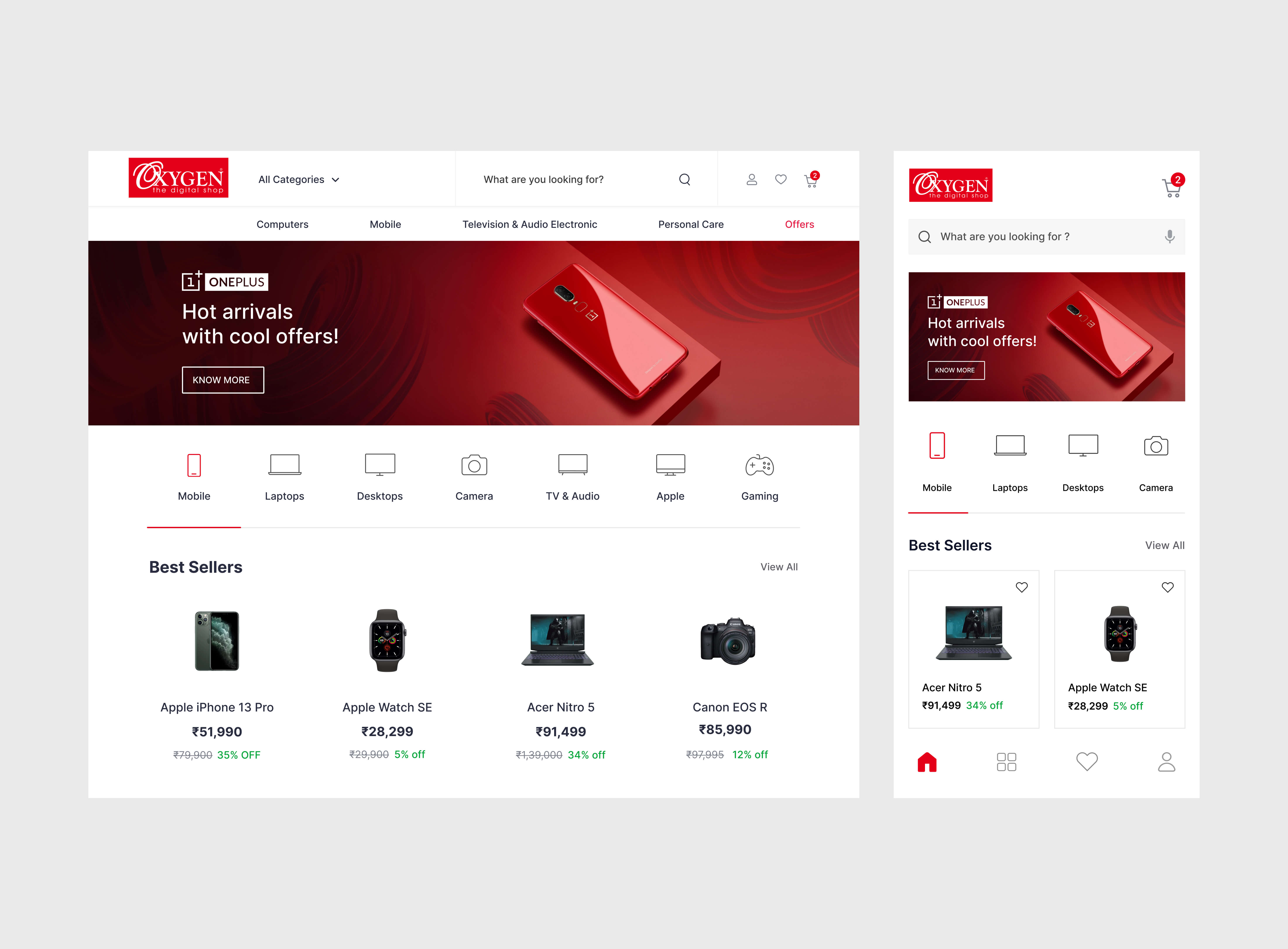
Taking care of your site’s checkout process can avoid cart abandonment, a common concern in ecommerce. The simplified checkout makes it straightforward and enhances user engagement. It is also important to integrate secure payment gateways with various payment options that accommodate the maximum number of potential customers. Implementing accessibility features also helps to create an inclusive platform that improves the customer experience.
3) Work on Building the Best Product Pages
You should be able to appeal to your customers and evoke their emotions effectively to build a high-end customer experience. While this is highly important to perform throughout the different marketing channels, it is also important to be made on product pages. Great product pages offer a perfect balance between offering all the information a customer needs to know about the product and the element that persuades them to purchase it.
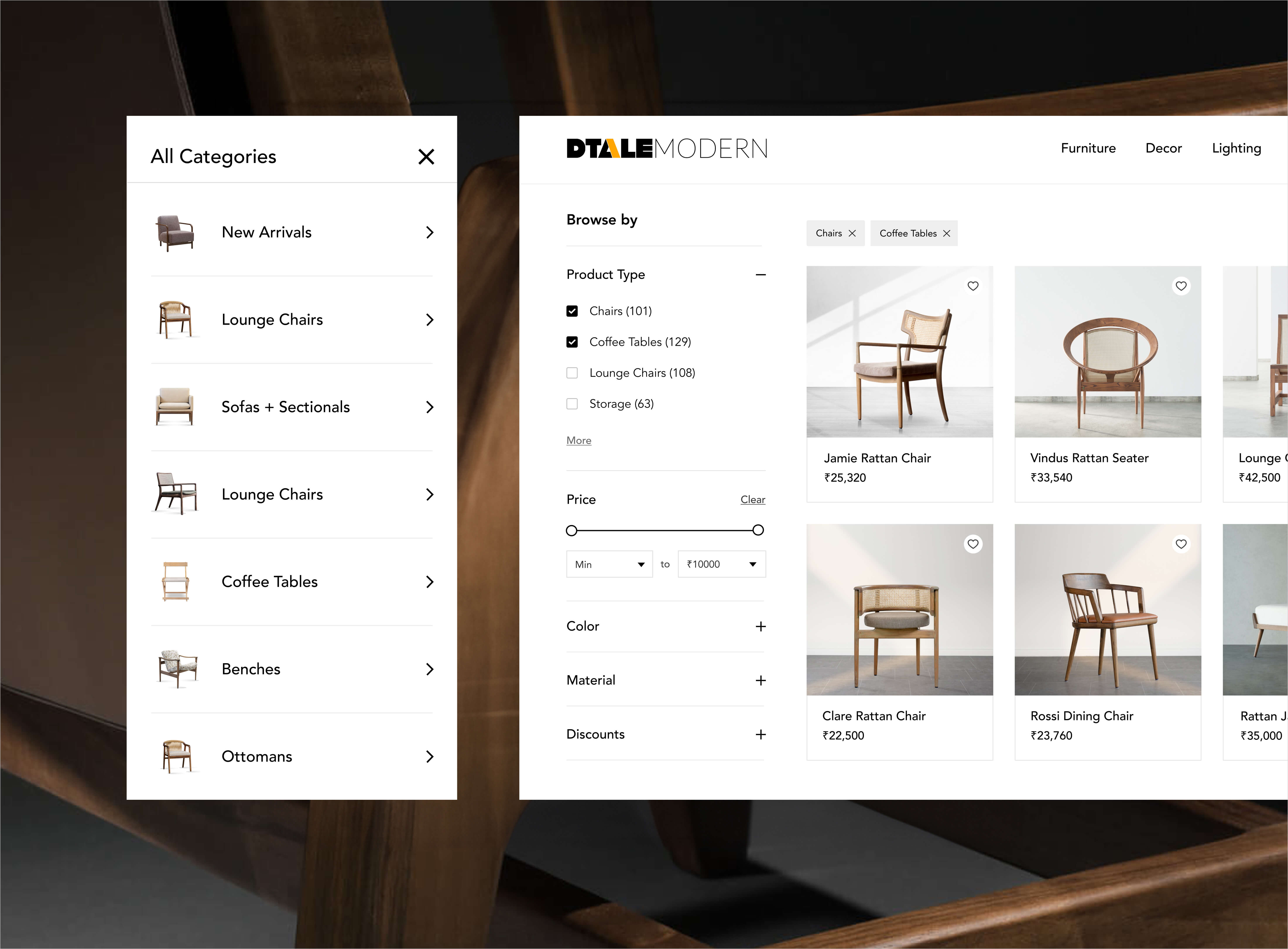
Product visuals with high-quality product images and explainer videos that describe the product are all various ways that help evoke the senses of a potential customer. Engaging your potential customers and giving them a stunning customer experience is the essence of your product page copy. Work on building a detailed description of the product features that let
customers understand how this product solves their problem.
4) Automate Repetitive Tasks
Automating repetitive tasks helps to free up the team’s time and lets them spend time on complex tasks or offer more proactive customer support. Automation boosts customer interactions for an improved customer experience, which helps streamline the team’s process. Order processing, inventory management, customer support and major phases of ecommerce can be made faster and more accurate through automation.
Chatbots can offer instant responses to common queries, which reduce wait times and enhance customer satisfaction. Extending this technology, an AI based call center ensures queries are quickly responded to, further enhances customer service. Personalised marketing with the help of automated email campaigns or recommendations can elevate the buying experience. Automated customer data analysis also helps you gather insights into customer behaviour, which lets businesses tailor services and promotions.
5) Omnichannel Retailing
Omnichannel retailing is becoming a growing necessity. With a great omnichannel experience, your customers can engage however they wish with your brand, on whichever platform or device they choose. It is important to take complete advantage of each channel your brand is active on and to understand how the channels evolve with time.
Integrating various channels helps customers avoid ‘starting over’ each time they engage with the brand. Instead, they can pick up right where they left off previously. The information that flows through different channels all filters to a unified location. This ensures that your CRM and other integrated tools are up-to-date every time, which minimises the chances of offering a redundant experience to the customers.
6) Enhance Loading Speed
Speed helps the customers load pages quickly and complete transactions without delay. Since slow-loading websites can cause frustration for customers and lead to cart abandonment, it impacts the bottom line.
To increase speed, make sure your website is performance-optimised, has a reliable hosting service and minimises latency, Track and test the load times of your site regularly to detect and address any possible bottlenecks. A seamless browsing experience lets customers stay engaged and be more likely to finish purchases.
7) Social Proof
Social proof is a reliable tool that builds the credibility of customers. With ratings, reviews and customers’ testimonials, you can influence their buying decisions. Portray customer feedback prominently on product pages and integrate user-generated content like photos, video posts, etc.
Showcase rewards or endorsements from reliable organisations that can let you portray the value of your brand. With social proof, you can evoke a sense of community, which persuades new customers to stay confident about their choices.
Bottom Line
Building a successful online store isn’t an overnight hurdle. Your primary focus should be customer loyalty and developing a great customer relationship, rather than creating a transaction. Finding the impact you’d like to create on your customers and the approach you would like to take to make them feel welcome helps you build a successful ecommerce customer experience.
By learning about various types of ecommerce, audiences and capabilities, you can choose a business model that works for you. After you find the ecommerce model that best fits your requirements, the next step is to get guidance from a reliable ecommerce development company offering the top ecommerce development services.
We are an Ecommerce Design Agency with experienced team of ecommerce specialists who can help you boost your ecommerce project by choosing the right business model, ecommerce consulting, custom ecommerce design and development, and marketing services.
Delve into the huge possibilities of ecommerce development services, including Shopify, Salesforce, Commercetools, SAP Hybris, BigCommerce, Woocommerce, and Adobe Commerce development services. To know more about how we work to propel your ecommerce business with various strategies, let’s discuss.

Looking for professional eCommerce development?
Bridge the gap between your storefront and customer with our strategic eCommerce solutions
- E-Commerce Statistics 2026: Key Trends, Growth Insights & Global Shopping Behavior
- Top Gen Z Shopping Trends Shaping eCommerce in 2026
- Adobe Commerce vs Commercetools: Choosing the Right eCommerce Platform for Scalable Success
- Composable Commerce in 2026: A Mainstream Solution for the Future of Retail
- E-commerce Trends That Are Powering Online Retail Forward In 2026
Discover Digital Transformation
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.










